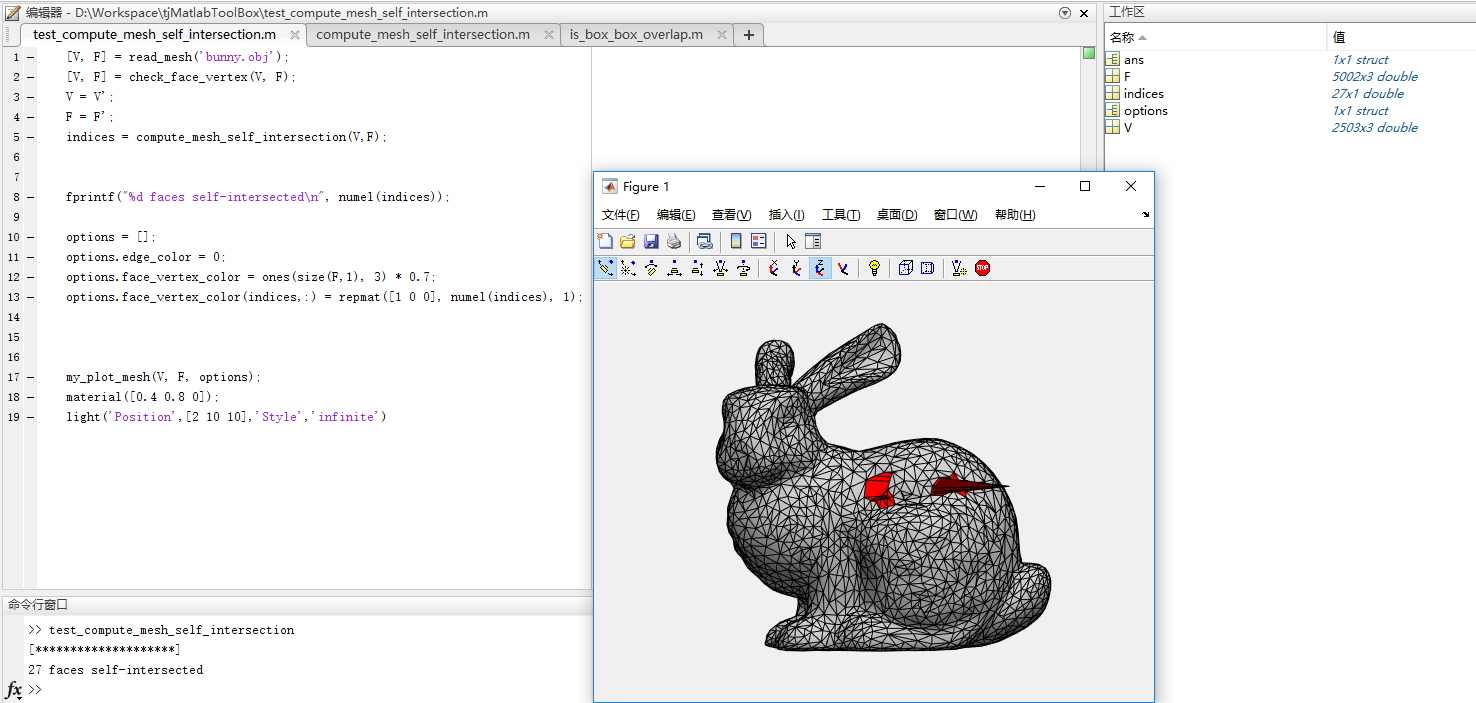
meshlab是基于vcglib写的, 最近需要检测mesh的自相交, 于是来看看它的源代码
static bool SelfIntersections(MeshType &m, std::vector<FaceType*> &ret)
{
RequirePerFaceMark(m);
ret.clear();
int referredBit = FaceType::NewBitFlag();
tri::UpdateFlags<MeshType>::FaceClear(m,referredBit);
TriMeshGrid gM;
gM.Set(m.face.begin(),m.face.end());
for(FaceIterator fi=m.face.begin();fi!=m.face.end();++fi) if(!(*fi).IsD())
{
(*fi).SetUserBit(referredBit);
Box3< ScalarType> bbox;
(*fi).GetBBox(bbox);
std::vector<FaceType*> inBox;
vcg::tri::GetInBoxFace(m, gM, bbox,inBox);
bool Intersected=false;
typename std::vector<FaceType*>::iterator fib;
for(fib=inBox.begin();fib!=inBox.end();++fib)
{
if(!(*fib)->IsUserBit(referredBit) && (*fib != &*fi) )
if(Clean<MeshType>::TestFaceFaceIntersection(&*fi,*fib)){
ret.push_back(*fib);
if(!Intersected) {
ret.push_back(&*fi);
Intersected=true;
}
}
}
inBox.clear();
}
FaceType::DeleteBitFlag(referredBit);
return (ret.size()>0);
}
对于每个面, 算个包围盒, 然后算出包围盒里面的面, 然后执行TestFaceFaceIntersection
static bool TestFaceFaceIntersection(FaceType *f0,FaceType *f1)
{
int sv = face::CountSharedVertex(f0,f1);
if(sv==3) return true;
if(sv==0) return (vcg::IntersectionTriangleTriangle<FaceType>((*f0),(*f1)));
// if the faces share only a vertex, the opposite edge (as a segment) is tested against the face
// to avoid degenerate cases where the two triangles have the opposite edge on a common plane
// we offset the segment to test toward the shared vertex
if(sv==1)
{
int i0,i1; ScalarType a,b;
face::FindSharedVertex(f0,f1,i0,i1);
CoordType shP = f0->V(i0)->P()*0.5;
if(vcg::IntersectionSegmentTriangle(Segment3<ScalarType>((*f0).V1(i0)->P()*0.5+shP,(*f0).V2(i0)->P()*0.5+shP), *f1, a, b) )
{
// a,b are the param coords of the intersection point of the segment.
if(a+b>=1 || a<=EPSIL || b<=EPSIL ) return false;
return true;
}
if(vcg::IntersectionSegmentTriangle(Segment3<ScalarType>((*f1).V1(i1)->P()*0.5+shP,(*f1).V2(i1)->P()*0.5+shP), *f0, a, b) )
{
// a,b are the param coords of the intersection point of the segment.
if(a+b>=1 || a<=EPSIL || b<=EPSIL ) return false;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
上面是检测两个面相交的算法:
先检测有几个共离点, 3个的话就判断为相交, 0的话就执行IntersectionTriangleTriangle,
1的话, 就用这个点的对边执行IntersectionSegmentTriangle
这里的segment加上了偏移,看英文 注释
接着看IntersectionTriangleTriangle
template<class T>
inline bool IntersectionTriangleTriangle(Point3<T> V0,Point3<T> V1,Point3<T> V2,
Point3<T> U0,Point3<T> U1,Point3<T> U2){
return NoDivTriTriIsect(V0,V1,V2,U0,U1,U2);
}
template<class T>
/*
@param V0 A vertex of the first triangle
@param V1 A vertex of the first triangle
@param V2 A vertex of the first triangle
@param U0 A vertex of the second triangle
@param U1 A vertex of the second triangle
@param U2 A vertex of the second triangle
@return true if the two triangles interesect
*/
bool NoDivTriTriIsect(const Point3<T> V0,const Point3<T> V1,const Point3<T> V2,
const Point3<T> U0,const Point3<T> U1,const Point3<T> U2)
{
Point3<T> E1,E2;
Point3<T> N1,N2;
T d1,d2;
T du0,du1,du2,dv0,dv1,dv2;
Point3<T> D;
T isect1[2], isect2[2];
T du0du1,du0du2,dv0dv1,dv0dv2;
short index;
T vp0,vp1,vp2;
T up0,up1,up2;
T bb,cc,max;
/* compute plane equation of triangle(V0,V1,V2) */
SUB(E1,V1,V0);
SUB(E2,V2,V0);
CROSS(N1,E1,E2);
N1.Normalize(); // aggiunto rispetto al codice orig.
d1=-DOT(N1,V0);
/* plane equation 1: N1.X+d1=0 */
/* put U0,U1,U2 into plane equation 1 to compute signed distances to the plane*/
du0=DOT(N1,U0)+d1;
du1=DOT(N1,U1)+d1;
du2=DOT(N1,U2)+d1;
/* coplanarity robustness check */
#ifdef USE_TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON_TEST
if(FABS(du0)<TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON) du0=0.0;
if(FABS(du1)<TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON) du1=0.0;
if(FABS(du2)<TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON) du2=0.0;
#endif
du0du1=du0*du1;
du0du2=du0*du2;
if(du0du1>0.0f && du0du2>0.0f) /* same sign on all of them + not equal 0 ? */
return 0; /* no intersection occurs */
/* compute plane of triangle (U0,U1,U2) */
SUB(E1,U1,U0);
SUB(E2,U2,U0);
CROSS(N2,E1,E2);
d2=-DOT(N2,U0);
/* plane equation 2: N2.X+d2=0 */
/* put V0,V1,V2 into plane equation 2 */
dv0=DOT(N2,V0)+d2;
dv1=DOT(N2,V1)+d2;
dv2=DOT(N2,V2)+d2;
#ifdef USE_TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON_TEST
if(FABS(dv0)<TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON) dv0=0.0;
if(FABS(dv1)<TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON) dv1=0.0;
if(FABS(dv2)<TRI_TRI_INT_EPSILON) dv2=0.0;
#endif
dv0dv1=dv0*dv1;
dv0dv2=dv0*dv2;
if(dv0dv1>0.0f && dv0dv2>0.0f) /* same sign on all of them + not equal 0 ? */
return 0; /* no intersection occurs */
/* compute direction of intersection line */
CROSS(D,N1,N2);
/* compute and index to the largest component of D */
max=(T)FABS(D[0]);
index=0;
bb=(T)FABS(D[1]);
cc=(T)FABS(D[2]);
if(bb>max) max=bb,index=1;
if(cc>max) max=cc,index=2;
/* this is the simplified projection onto L*/
vp0=V0[index];
vp1=V1[index];
vp2=V2[index];
up0=U0[index];
up1=U1[index];
up2=U2[index];
/* compute interval for triangle 1 */
T a,b,c,x0,x1;
NEWCOMPUTE_INTERVALS(vp0,vp1,vp2,dv0,dv1,dv2,dv0dv1,dv0dv2,a,b,c,x0,x1);
/* compute interval for triangle 2 */
T d,e,f,y0,y1;
NEWCOMPUTE_INTERVALS(up0,up1,up2,du0,du1,du2,du0du1,du0du2,d,e,f,y0,y1);
T xx,yy,xxyy,tmp;
xx=x0*x1;
yy=y0*y1;
xxyy=xx*yy;
tmp=a*xxyy;
isect1[0]=tmp+b*x1*yy;
isect1[1]=tmp+c*x0*yy;
tmp=d*xxyy;
isect2[0]=tmp+e*xx*y1;
isect2[1]=tmp+f*xx*y0;
SORT(isect1[0],isect1[1]);
SORT(isect2[0],isect2[1]);
if(isect1[1]<isect2[0] || isect2[1]<isect1[0]) return 0;
return 1;
}
这个算法详细请看论文 A Fast Triangle-Triangle Intersection Test
https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs277/resources/papers/Moller1997b.pdf
原理就是公式(4), 这里的代码在两边同时乘以了
#define NEWCOMPUTE_INTERVALS(VV0,VV1,VV2,D0,D1,D2,D0D1,D0D2,A,B,C,X0,X1) \
{ \
if(D0D1>0.0f) \
{ \
/* here we know that D0D2<=0.0 */ \
/* that is D0, D1 are on the same side, D2 on the other or on the plane */ \
A=VV2; B=(VV0-VV2)*D2; C=(VV1-VV2)*D2; X0=D2-D0; X1=D2-D1; \
} \
else if(D0D2>0.0f)\
{ \
/* here we know that d0d1<=0.0 */ \
A=VV1; B=(VV0-VV1)*D1; C=(VV2-VV1)*D1; X0=D1-D0; X1=D1-D2; \
} \
else if(D1*D2>0.0f || D0!=0.0f) \
{ \
/* here we know that d0d1<=0.0 or that D0!=0.0 */ \
A=VV0; B=(VV1-VV0)*D0; C=(VV2-VV0)*D0; X0=D0-D1; X1=D0-D2; \
} \
else if(D1!=0.0f) \
{ \
A=VV1; B=(VV0-VV1)*D1; C=(VV2-VV1)*D1; X0=D1-D0; X1=D1-D2; \
} \
else if(D2!=0.0f) \
{ \
A=VV2; B=(VV0-VV2)*D2; C=(VV1-VV2)*D2; X0=D2-D0; X1=D2-D1; \
} \
else \
{ \
/* triangles are coplanar */ \
return coplanar_tri_tri(N1,V0,V1,V2,U0,U1,U2); \
} \
}
再来看看两个三角形共面的情形
template<class T>
/** CHeck two triangles for coplanarity
@param N
@param V0 A vertex of the first triangle
@param V1 A vertex of the first triangle
@param V2 A vertex of the first triangle
@param U0 A vertex of the second triangle
@param U1 A vertex of the second triangle
@param U2 A vertex of the second triangle
@return true se due triangoli sono cooplanari, false altrimenti
*/
bool coplanar_tri_tri(const Point3<T> N, const Point3<T> V0, const Point3<T> V1,const Point3<T> V2,
const Point3<T> U0, const Point3<T> U1,const Point3<T> U2)
{
T A[3];
short i0,i1;
/* first project onto an axis-aligned plane, that maximizes the area */
/* of the triangles, compute indices: i0,i1. */
A[0]=FABS(N[0]);
A[1]=FABS(N[1]);
A[2]=FABS(N[2]);
if(A[0]>A[1])
{
if(A[0]>A[2])
{
i0=1; /* A[0] is greatest */
i1=2;
}
else
{
i0=0; /* A[2] is greatest */
i1=1;
}
}
else /* A[0]<=A[1] */
{
if(A[2]>A[1])
{
i0=0; /* A[2] is greatest */
i1=1;
}
else
{
i0=0; /* A[1] is greatest */
i1=2;
}
}
/* test all edges of triangle 1 against the edges of triangle 2 */
EDGE_AGAINST_TRI_EDGES(V0,V1,U0,U1,U2);
EDGE_AGAINST_TRI_EDGES(V1,V2,U0,U1,U2);
EDGE_AGAINST_TRI_EDGES(V2,V0,U0,U1,U2);
/* finally, test if tri1 is totally contained in tri2 or vice versa */
POINT_IN_TRI(V0,U0,U1,U2);
POINT_IN_TRI(U0,V0,V1,V2);
return 0;
}
#define EDGE_AGAINST_TRI_EDGES(V0,V1,U0,U1,U2) \
{ \
T Ax,Ay,Bx,By,Cx,Cy,e,d,f; \
Ax=V1[i0]-V0[i0]; \
Ay=V1[i1]-V0[i1]; \
/* test edge U0,U1 against V0,V1 */ \
EDGE_EDGE_TEST(V0,U0,U1); \
/* test edge U1,U2 against V0,V1 */ \
EDGE_EDGE_TEST(V0,U1,U2); \
/* test edge U2,U1 against V0,V1 */ \
EDGE_EDGE_TEST(V0,U2,U0); \
}
先用边检测是否相交于三角形, 如果不相交再检测整个三角形是否在另一个三角形里面(只需要检测一个点即可)
#define EDGE_EDGE_TEST(V0,U0,U1) \
Bx=U0[i0]-U1[i0]; \
By=U0[i1]-U1[i1]; \
Cx=V0[i0]-U0[i0]; \
Cy=V0[i1]-U0[i1]; \
f=Ay*Bx-Ax*By; \
d=By*Cx-Bx*Cy; \
if((f>0 && d>=0 && d<=f) || (f<0 && d<=0 && d>=f)) \
{ \
e=Ax*Cy-Ay*Cx; \
if(f>0) \
{ \
if(e>=0 && e<=f) return 1; \
} \
else \
{ \
if(e<=0 && e>=f) return 1; \
} \
}
边检测原理
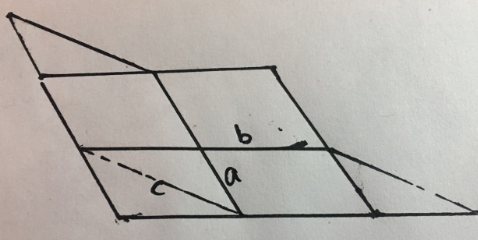
原理就是如果a,b相交, 那么 ab形成的四边形面积要比ac和bc形成的面积要大
并且b->a 和 c->b以及a->c所指的方向 应该一样
#define POINT_IN_TRI(V0,U0,U1,U2) \
{ \
T a,b,c,d0,d1,d2; \
/* is T1 completly inside T2? */ \
/* check if V0 is inside tri(U0,U1,U2) */ \
a=U1[i1]-U0[i1]; \
b=-(U1[i0]-U0[i0]); \
c=-a*U0[i0]-b*U0[i1]; \
d0=a*V0[i0]+b*V0[i1]+c; \
\
a=U2[i1]-U1[i1]; \
b=-(U2[i0]-U1[i0]); \
c=-a*U1[i0]-b*U1[i1]; \
d1=a*V0[i0]+b*V0[i1]+c; \
\
a=U0[i1]-U2[i1]; \
b=-(U0[i0]-U2[i0]); \
c=-a*U2[i0]-b*U2[i1]; \
d2=a*V0[i0]+b*V0[i1]+c; \
if(d0*d1>0.0) \
{ \
if(d0*d2>0.0) return 1; \
} \
}
最后来看检测一个点是否在三角形内
提出a,b可得知
就是检测U0V0和U0U1的叉乘 d0
U1V0和U1U2的叉乘d1
U2V0和U2U0的叉乘d2
三个方向一致

最后看下, 线段与三角形的相交
/**
* Compute the intersection between a segment and a triangle.
* It relies on the lineTriangle Intersection
* @param[in] segment
* @param[in] triangle vertices
* @param[out]=(t,u,v) the intersection point, meaningful only if the line of segment intersects the triangle
* t is the baricentric coord of the point on the segment
* (u,v) are the baricentric coords of the intersection point in the segment
*
*/
template<class ScalarType>
bool IntersectionSegmentTriangle( const vcg::Segment3<ScalarType> & seg,
const Point3<ScalarType> & vert0,
const Point3<ScalarType> & vert1, const
Point3<ScalarType> & vert2,
ScalarType & a ,ScalarType & b)
{
//control intersection of bounding boxes
vcg::Box3<ScalarType> bb0,bb1;
bb0.Add(seg.P0());
bb0.Add(seg.P1());
bb1.Add(vert0);
bb1.Add(vert1);
bb1.Add(vert2);
Point3<ScalarType> inter;
if (!bb0.Collide(bb1))
return false;
if (!vcg::IntersectionSegmentBox(bb1,seg,inter))
return false;
//first set both directions of ray
vcg::Line3<ScalarType> line;
vcg::Point3<ScalarType> dir;
ScalarType length=seg.Length();
dir=(seg.P1()-seg.P0());
dir.Normalize();
line.Set(seg.P0(),dir);
ScalarType orig_dist;
if(IntersectionLineTriangle<ScalarType>(line,vert0,vert1,vert2,orig_dist,a,b))
return (orig_dist>=0 && orig_dist<=length);
return false;
}
/*
* Function computing the intersection between a line and a triangle.
* from:
* Tomas Moller and Ben Trumbore,
* ``Fast, Minimum Storage Ray-Triangle Intersection'',
* journal of graphics tools, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 21-28, 1997
* @param[in] line
* @param[in] triangle vertices
* @param[out]=(t,u,v) the intersection point, meaningful only if the line intersects the triangle
* t is the line parameter and
* (u,v) are the baricentric coords of the intersection point
*
* Line.Orig + t * Line.Dir = (1-u-v) * Vert0 + u * Vert1 +v * Vert2
*
*/
template<class T>
bool IntersectionLineTriangle( const Line3<T> & line, const Point3<T> & vert0,
const Point3<T> & vert1, const Point3<T> & vert2,
T & t ,T & u, T & v)
{
#define EPSIL 0.000001
vcg::Point3<T> edge1, edge2, tvec, pvec, qvec;
T det,inv_det;
/* find vectors for two edges sharing vert0 */
edge1 = vert1 - vert0;
edge2 = vert2 - vert0;
/* begin calculating determinant - also used to calculate U parameter */
pvec = line.Direction() ^ edge2;
/* if determinant is near zero, line lies in plane of triangle */
det = edge1 * pvec;
/* calculate distance from vert0 to line origin */
tvec = line.Origin() - vert0;
inv_det = 1.0 / det;
qvec = tvec ^ edge1;
if (det > EPSIL)
{
u = tvec * pvec ;
if ( u < 0.0 || u > det)
return 0;
/* calculate V parameter and test bounds */
v = line.Direction() * qvec;
if ( v < 0.0 || u + v > det)
return 0;
}
else if(det < -EPSIL)
{
/* calculate U parameter and test bounds */
u = tvec * pvec ;
if ( u > 0.0 || u < det)
return 0;
/* calculate V parameter and test bounds */
v = line.Direction() * qvec ;
if ( v > 0.0 || u + v < det)
return 0;
}
else return 0; /* line is parallell to the plane of the triangle */
t = edge2 * qvec * inv_det;
( u) *= inv_det;
( v) *= inv_det;
return 1;
}
原理请见fast minimum storage ray-triangle intersection
https://cadxfem.org/inf/Fast MinimumStorage RayTriangle Intersection.pdf
最后用meshlab验证自已的实现结果