测试用的树
private static void SetSubTreeNode(Node root, Node leftChild, Node rightChild)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
root.leftChild= leftChild;
root.rightChild = rightChild;
}
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// /\ \
// 4 5 6
// /
// 7
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(2);
Node node3 = new Node(3);
Node node4 = new Node(4);
Node node5 = new Node(5);
Node node6 = new Node(6);
Node node7 = new Node(7);
SetSubTreeNode(node1, node2, node3);
SetSubTreeNode(node2, node4, node5);
SetSubTreeNode(node3, null, node6);
SetSubTreeNode(node5, node7, null);
1.二叉数数据结构
//1。二叉树数据结构
class Node {
public Object data;//节点数据
public Node leftChild;//左子节点的引用
public Node rightChild;//右子节点的引用
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
leftChild = null;
rightChild = null;
}
}
2.递归——求二叉树的深度
//2.递归——求二叉树深度
public static int maxtreeDepth(Node root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = maxtreeDepth(root.leftChild);
int right = maxtreeDepth(root.rightChild);
return (left>right)?(left+1):(right+1);
}
结果:

3.递归——求二叉树的最小深度
//3.递归——求二叉树的最小深度
public static int mintreeDepth(Node root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = mintreeDepth(root.leftChild);
int right = mintreeDepth(root.rightChild);
if(left == 0 && right > 0) return right+1;
else if(right == 0 && left > 0) return left+1;
else return (left < right) ? (left+1) : (right+1);
}
结果

4.求二叉树中节点的个数
//4.求二叉树中节点的个数
public static int sumNode(Node root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = sumNode(root.leftChild);
int right = sumNode(root.rightChild);
return 1+left+right;
}
结果

5.求二叉树中叶子节点的个数
//5.求二叉树中叶子节点的个数
public static int numLeaf(Node root){
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) flag++;
numLeaf(root.leftChild);
numLeaf(root.rightChild);
return flag;
}

6.求二叉树中第k层节点的个数
//6.求二叉树中第k层节点的个数
public static int KLevelLeafNode(Node root,int KLevel){
if(root == null || KLevel <= 0) return 0;
if(root != null && KLevel == 1) return 1;
return (KLevelLeafNode(root.leftChild,KLevel-1)+KLevelLeafNode(root.rightChild,KLevel-1));
}
结果:

7.判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
//7.判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
//平衡二叉树就是左子树和右子树的高度差不能超过1,且左右子树必须是平衡二叉树;
public static boolean IsBalanced(Node root){
if(root == null) return true;
if(Math.abs(maxtreeDepth(root.leftChild) - maxtreeDepth(root.rightChild))<=1){
//满足左右子树高度差小于等于1,接着判断左右子树是不是二叉树
return (IsBalanced(root.leftChild) && IsBalanced(root.rightChild));
}else{
return false;
}
}

8.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
//8.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
/*
* 判断一个树是否属于完全二叉树可以从以下2个条件来判断:
层次遍历二叉树
1 任何一个结点如果右孩子不为空,左孩子却是空,则一定不是完全二叉树
2 当一个结点出现右孩子为空时候,判断该结点的层次遍历后继结点是否为叶子节点,
如果全部都是叶子节点,则是完全二叉树,如果存在任何一个结点不是叶节点,则一定不是完全二叉树。
*/
public static boolean isCBT(Node node){
if(node == null) return false;
Node leftChild = null;
Node rightChild = null;
boolean left = false;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.offer(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node head = queue.poll();
leftChild = head.leftChild;
rightChild = head.rightChild;
//右孩子不等于空,左孩子等于空 -> false
if((rightChild != null && leftChild == null)
||
//开启叶节点判断标志位时,如果层次遍历中的后继结点不是叶节点 -> false
(left &&(rightChild != null || leftChild != null))){
return false;
}
if(leftChild != null){
queue.offer(leftChild);
}
if(rightChild != null){
queue.offer(rightChild);
}
else{
left = true;
}
}
return true;
}
结果
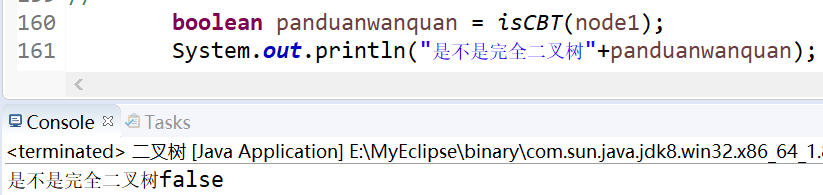
9.两个二叉树是否完全相同
//9.两个二叉树是否完全相同
/*
* 思想:如果两颗树都为空则相同
* 如果其中一棵树为空,则不同
* 如果两颗谁都不为空,则判断左右子树是否相同
*/
public static boolean IsSame(Node first,Node second){
if(first == null && second == null) return true;
else if(first == null || second == null) return false;
if(first != null && second != null){
if(first.data != second.data) return false;
else return IsSame(first.leftChild,second.leftChild) && IsSame(first.rightChild,second.rightChild);
}
return false;
}
结果

10.两个二叉树是否互为镜像(对称)
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
6102201 查看本文章


//10.两个二叉树是否互为镜像(对称)
/*
* 思想是:
* 首先判断这棵树是否为空树,如果空树则直接返回true
* 如果不为空,则在进行分类:
* case1:节点的左右子树为空,则直接返回true
* case2:节点的左右子树有一个为空,则直接返回false
* case3:节点的左右子树均不为空,则判断节点的左右子节点的值是否相等
* 并且判断左节点的子左节点和右节点的右子节点是否对称
* 还有左节点的右子节点和右节点的左子节点是否对称
*/
public static boolean IsSymmetry(Node root){
if(root == null) return true;
return IsSymmetry(root.leftChild,root.rightChild);
}
public static boolean IsSymmetry(Node left,Node right){
if(left == null && right == null) return true;
if(left == null || right == null) return false;
return left.data == right.data && IsSymmetry(left.leftChild,right.rightChild)&&IsSymmetry(left.rightChild,right.leftChild);
}

11.翻转二叉树or镜像二叉树
public static Node invertTree(Node root){
if(root == null) return null;
Node left = invertTree(root.leftChild);
Node right = invertTree(root.rightChild);
root.leftChild = right;
root.rightChild = left;
return root;
}
结果:

12.求两个二叉树的最低公共祖先节点
public static Node findParent(Node root,Node node1,Node node2){
if(findNode(root.leftChild,node1)){
if(findNode(root.rightChild,node2)) return root;
else return findParent(root.leftChild,node1,node2);
}
else{
if(findNode(root.leftChild,node2)) return root;
else return findParent(root.rightChild,node1,node2);
}
}
public static boolean findNode(Node root,Node node){
if(root == null || node == null) return false;
if(root == node) return true;
boolean found = findNode(root.leftChild,node);
if(!found) found = findNode(root.rightChild,node);
return found;
}
13.二叉树的前序遍历
//递归解法
public static ArrayList<Integer> preOrderReverse(Node root){
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preOrder2(root,result);
return result;
}
public static void preOrder2(Node root,ArrayList<Integer> result){
if(root == null) return;
result.add((Integer) root.data);
preOrder2(root.leftChild,result);
preOrder2(root.rightChild,result);
}
//迭代
public static ArrayList<Integer> preOrder(Node root){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root == null) return list;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()){
Node node = stack.pop();
list.add((Integer) node.data);
if(node.rightChild != null) stack.push(node.rightChild);
if(node.leftChild != null) stack.push(node.leftChild);
}
return list;
}
结果:

14.二叉树的中序遍历
public static ArrayList<Integer> inOrder(Node root){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node current = root;
while(current != null ||!stack.empty()){
while(current != null){
stack.add(current);
current = current.leftChild;
}
current = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
list.add((Integer) current.data);
current = current.rightChild;
}
return list;
}
结果:
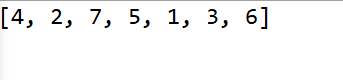
15.二叉树的后序遍历
public static ArrayList<Integer> postOrder(Node root){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root == null) return list;
list.addAll(postOrder(root.leftChild));
list.addAll(postOrder(root.rightChild));
list.add((Integer) root.data);
return list;
}
结果:
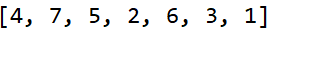
16.前序遍历和后序遍历构造二叉树
public static Node buildTreeNode(int[] preorder,int[] inorder){
if(preorder.length != inorder.length) return null;
return myBuildTree(preorder,0,preorder.length-1,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public static Node myBuildTree(int[] preorder,int prestart,int preend,int[] inorder,int instart,int inend){
if(instart>inend || prestart > preend) return null;
Node root = new Node(preorder[prestart]);
for(int i = instart;i<=inend;i++){
if(inorder[i] == preorder[prestart]){
root.leftChild = myBuildTree(preorder,prestart+1,prestart+i-instart,inorder,instart,i-1);
root.rightChild = myBuildTree(preorder,i-instart+prestart+1,preend,inorder,i+1,inend);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
结果:
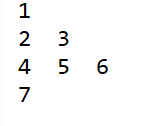
17.在二叉树中插入节点
public static Node insertNode(Node root,Node node){
if(root == node) return node;
Node tmp = root;
Node last = null;
while(tmp != null){
last = tmp;
if((int)tmp.data>(int)tmp.data) tmp = tmp.leftChild;
else tmp = tmp.rightChild;
}
if(last != null){
if((int)last.data > (int)node.data) last.leftChild = node;
else last.rightChild = node;
}
return root;
}
结果:
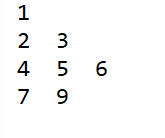
18.输入一个二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和等于输入整数所有的路径
//18.输入一个二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和等于输入整数所有的路径
public static void findPath(Node root,int i){
if(root == null) return;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
int currentSum = 0;
findPath(root,i,stack,currentSum);
}
public static void findPath(Node root,int i,Stack<Integer> stack,int currentSum){
currentSum +=(int) root.data;
stack.push((int)root.data);
if(root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null){
if(currentSum == i){
for(int path:stack){
System.out.println(path);
}
}
}
if(root.leftChild != null) findPath(root.leftChild,i,stack,currentSum);
if(root.rightChild != null) findPath(root.rightChild,i,stack,currentSum);
stack.pop();
}
findPath(node1,10);
结果:

19.二叉树的搜索区间
20.二叉树的层次遍历
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root){
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if(root == null) return result;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
ArrayList<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i= 0;i<size;i++){
Node node = queue.poll();
level.add((int)node.data);
if(node.leftChild != null) queue.offer(node.leftChild);
if(node.rightChild != null) queue.offer(node.rightChild);
}
result.add(level);
}
return result;
}
结果:
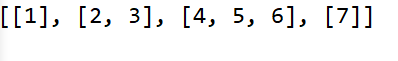
21.二叉树内两个节点的最长距离
public static class Result{
int maxDistance;
int maxDepth;
public Result(){
}
public Result(int maxDistance,int maxDepth){
this.maxDepth = maxDepth;
this.maxDistance = maxDistance;
}
}
static int getMaxDistance(Node root){
return getMaxDistanceResult(root).maxDistance;
}
static Result getMaxDistanceResult(Node root){
if(root == null){
Result empty = new Result(0,-1);
return empty;
}
Result lmd = getMaxDistanceResult(root.leftChild);
Result rmd = getMaxDistanceResult(root.rightChild);
Result result = new Result();
result.maxDepth = Math.max(lmd.maxDepth,rmd.maxDepth)+1;
result.maxDistance = Math.max(lmd.maxDepth+rmd.maxDepth, Math.max(lmd.maxDistance, rmd.maxDistance));
return result;
}
结果:

22.不同的二叉树
public static int numTrees(int n){
int[] counts = new int[n+2];
counts[0] = 1;
counts[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<i;j++){
counts[i] += counts[j]*counts[i-j-1];
}
}
return counts[n];
}
23.判断二叉树是否是合法的二叉查找树(BST)
public static int lastVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static boolean firstNode = true;
public static boolean isValidBST(Node root){
if(root == null) return true;
if(!isValidBST(root.leftChild)) return false;
if(!firstNode &&lastVal>=(int)root.data) return false;
firstNode = false;
lastVal = (int)root.data;
if(!isValidBST(root.rightChild)) return false;
return true;
}
结果:
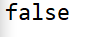
参考:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fMbV2cG8so5K2vi0N7DaTw
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34120430/article/details/80043472