算法 - 比赛得分可能数
1 介绍
2 实现
2.1 分析
2.2 算法一
2.3 算法二
2.4 算法三
1 介绍
以排球比赛分例,默认情况下,A、B 两队比赛时,率先得到 25 分得将取胜。但若双方打成 24:24 时,则最高得分将变为 26 分。以后情况以此类推,例如,理论上可以打出诸如 40:42 这样的结局。
算法的要求是,在已知最终比分的情况下,算出能够达到该最终比分的所有可能得分顺序。
例1:如果最终比分是 0:25,那么只有一种顺序,那就是:
0:1 → 0:2 → 0:3 → ... 0:24 → 0:25
例2:如果最终比分是 1:25,那么可能有 25 种情况,例如:
1:0 → 0:1 → 0:2 → 0:3 → ... 0:24 → 0:25
0:1 → 1:1 → 1:2 → 1:3 → ... 1:24 → 1:25
0:1 → 0:2 → 1:2 → 1:3 → ... 1:24 → 1:25
......
例3:如果最终比分是 3:25,将有 2925 种情况
例4:如果最终比分是 3:12,结果为 0,因为不可能有这种情况的最终比分
要求编写程序实现该功能,可以支持的最大比分数为 40。
2 实现
2.1 分析
很容易想到,比赛的可能路径可以使用如下的二叉树来分析,红色节点表示为不可能的分支
本例中的算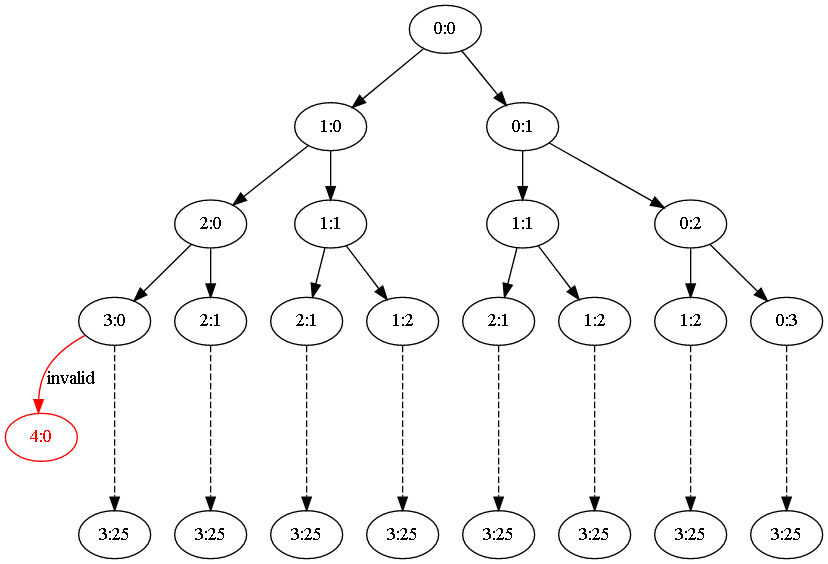 法使用 C# 实现
法使用 C# 实现
首先不管算法如何,先把一些公共的判断函数写在这里,以后其它例子都会用
// 是否有效最终比分
const int MAX = 25; static bool IsValid(int A, int B) { if (A < MAX && B < MAX) { return false; } if (Math.Abs(A - B) < 2) { return false; } if (Math.Max(A, B) > MAX && Math.Abs(A - B) != 2) { return false; } return true; } // 是否为有效中间比分,例如如果最终比分为 3:25,中间不可能出现 2:25(已经赢了不用再打了) static bool IsValidPath(int A, int B, int finalA, int finalB) { if (A > finalA || B > finalB) { return false; } if (IsWinStatus(A, B)) { return A == finalA && B == finalB; } else { return true; } } // 是否获胜 static bool IsWinStatus(int A, int B) { if (Math.Max(A, B) == MAX && Math.Abs(A - B) >= 2) { return true; } if (Math.Max(A, B) > MAX && Math.Abs(A - B) == 2) { return true; } return false; }
2.2 算法一
很容易想到第一种算法,就是试图生成上图中的二叉树,如果生成出一个最终叶子结点(例如 3:25)则将计数器加 1,如下所示
class Model1
{
static void Main(string[] args) { int a = CalcScore1(7, 25); Console.WriteLine("Result: " + a); Console.Read(); } // 计算可能得分的入口函数 static int CalcScore1(int A, int B) { if (!IsValid(A, B)) { return 0; } Node rootNode = new Node(0, 0); int counter = 0; Constuct(rootNode, A, B, ref counter); return counter; } private static void Constuct(Node node, int finalA, int finalB, ref int counter) { if (node.ValueA == finalA && node.ValueB == finalB) { counter++; } else { if (node.ValueA < finalA && IsValidPath(node.ValueA + 1, node.ValueB, finalA, finalB)) { node.Left = new Node(node.ValueA + 1, node.ValueB); } if (node.ValueB < finalB && IsValidPath(node.ValueA, node.ValueB + 1, finalA, finalB)) { node.Right = new Node(node.ValueA, node.ValueB + 1); } } if (node.Left != null) { Constuct(node.Left, finalA, finalB, ref counter); } if (node.Right != null) { Constuct(node.Right, finalA, finalB, ref counter); } } class Node { public Node(int A, int B) { this.ValueA = A; this.ValueB = B; } public int ValueA { get; set; } public int ValueB { get; set; } public Node Left { get; set; } public Node Right { get; set