版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/YunLaowang/article/details/87714576
本文为参考【计算机视觉life】公众号的系列文章:从零开始一起学习SLAM | 点云到网格的进化,实现的点云网格化过程。
网格化流程
- 下采样+统计滤波
通过下采样减少点云数据容量、提高处理速度;使用统计分析技术,去除点云数据集中的噪声、离群点;
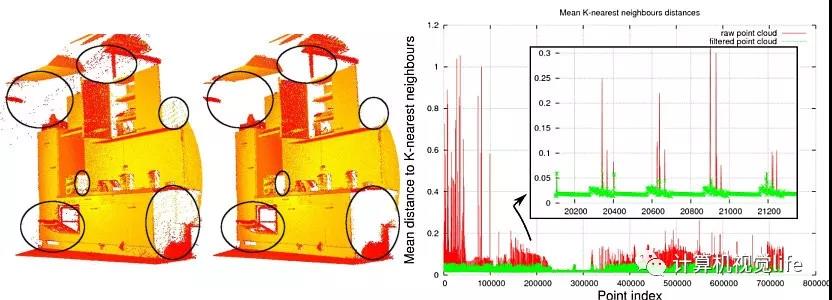
滤波前后对比
- 重采样,平滑处理
通过重采样对物体表面进行平滑处理和漏洞修复
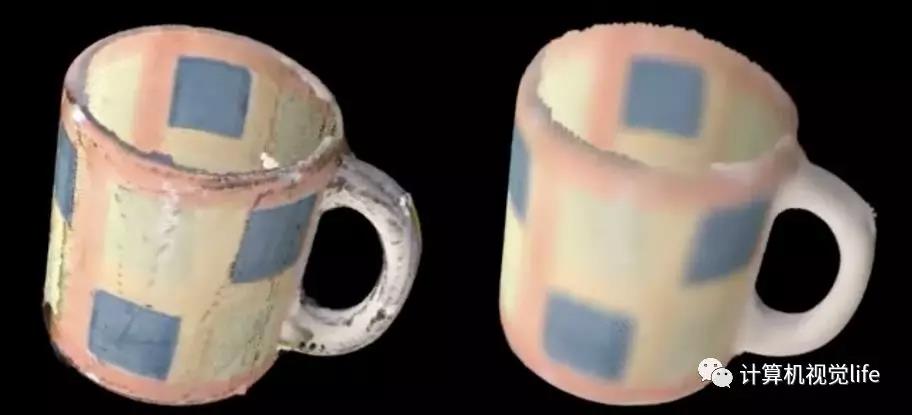

点云平滑前后
- 计算点云表面法线
计算点云法线,并将点云位姿、颜色、法线信息合并到一起,构建有向点云。
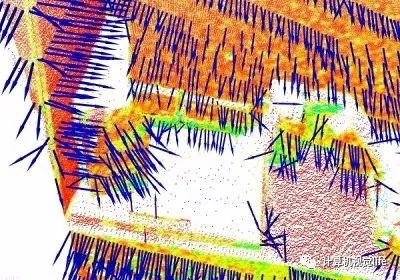
点云表面法线
- 网格化
使用贪心投影三角化算法对有向点云进行三角化,实现稀疏点云的网格化。
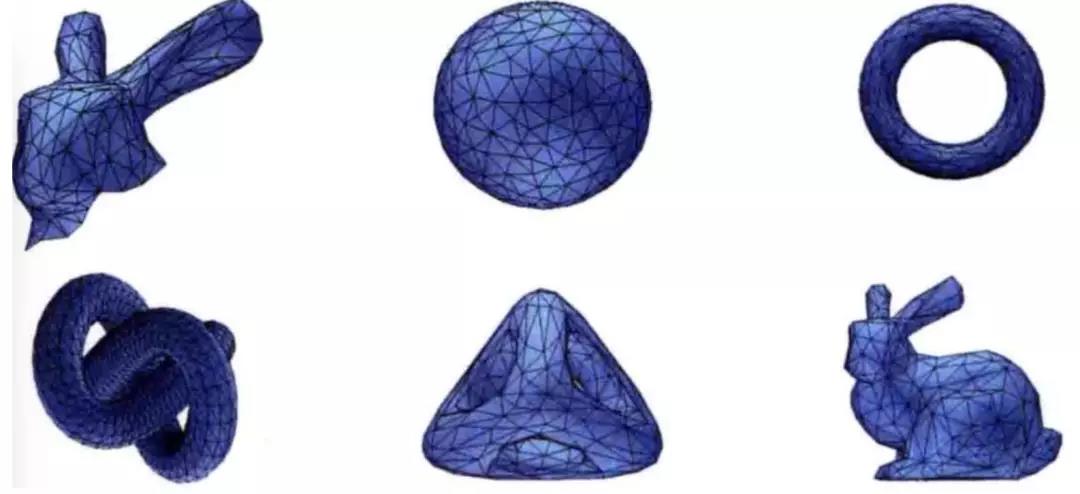
点云网格化示例
代码
/****************************
* 给定稠密的点云,进行如下操作:
* 下采样和滤波、重采样平滑、法线计算,贪心投影网格化。
****************************/
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/filters/radius_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/surface/mls.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/surface/gp3.h>
#include <pcl/surface/poisson.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// Load input file
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_downSampled(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_smoothed(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("fusedCloud.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
cout << "could not load the file..." << endl;
}
std::cout << "Orginal points number: " << cloud->points.size() << std::endl;
// 1.下采样,同时保持点云形状特征
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> downSampled; // 下采样对象
downSampled.setInputCloud(cloud);
downSampled.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f); // 栅格叶的尺寸
downSampled.filter(*cloud_downSampled);
// 2.统计滤波
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> sor; // 滤波对象
sor.setInputCloud(cloud_downSampled);
sor.setMeanK(50);
sor.setStddevMulThresh(1.0); // 设置判定为离群点的阈值
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
// 3.对点云重采样,进行平滑
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr treeSampling(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>); // 创建用于最近邻搜索的KD-Tree
pcl::MovingLeastSquares<PointT, PointT> mls; // 定义最小二乘实现的对象mls
mls.setComputeNormals(false); // 设置在最小二乘计算中是否需要存储计算的法线
mls.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); // 设置待处理点云
mls.setPolynomialOrder(2); // 拟合2阶多项式拟合
mls.setPolynomialFit(false); // 设置为false可以 加速 smooth
mls.setSearchMethod(treeSampling); // 设置KD-Tree作为搜索方法
mls.setSearchRadius(0.05); // 单位m.设置用于拟合的K近邻半径
mls.process(*cloud_smoothed); // 输出
// 4.法线估计
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, pcl::Normal> normalEstimation; // 创建法线估计的对象
normalEstimation.setInputCloud(cloud_smoothed); // 输入点云
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>); // 创建用于最近邻搜索的KD-Tree
normalEstimation.setSearchMethod(tree);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>); // 定义输出的点云法线
// K近邻确定方法,使用k个最近点,或者确定一个以r为半径的圆内的点集来确定都可以,两者选1即可
normalEstimation.setKSearch(10); // 使用当前点周围最近的10个点
//normalEstimation.setRadiusSearch(0.03); // 对于每一个点都用半径为3cm的近邻搜索方式
normalEstimation.compute(*normals); // 计算法线
// 5.将点云位姿、颜色、法线信息连接到一起
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud_smoothed, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);
// 6.贪心投影三角化
//定义搜索树对象
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr tree2(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>);
tree2->setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);
// 三角化
pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation<pcl::PointNormal> gp3; // 定义三角化对象
pcl::PolygonMesh triangles; // 存储最终三角化的网络模型
// 设置三角化参数
gp3.setSearchRadius(0.1); // 设置搜索时的半径,也就是KNN的球半径
gp3.setMu(2.5); // 设置样本点搜索其近邻点的最远距离为2.5倍(典型值2.5-3),这样使得算法自适应点云密度的变化
gp3.setMaximumNearestNeighbors(100); // 设置样本点最多可搜索的邻域个数,典型值是50-100
gp3.setMinimumAngle(M_PI / 18); // 设置三角化后得到的三角形内角的最小的角度为10°
gp3.setMaximumAngle(2 * M_PI / 3); // 设置三角化后得到的三角形内角的最大角度为120°
gp3.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI / 4); // 设置某点法线方向偏离样本点法线的最大角度45°,如果超过,连接时不考虑该点
gp3.setNormalConsistency(false); // 设置该参数为true保证法线朝向一致,设置为false的话不会进行法线一致性检查
gp3.setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals); // 设置输入点云为有向点云
gp3.setSearchMethod(tree2); // 设置搜索方式
gp3.reconstruct(triangles); // 重建提取三角化
// 7.显示网格化结果
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0); // 设置背景
viewer->addPolygonMesh(triangles, "mesh"); // 网格化点云添加到视窗
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
return 1;
}
结果
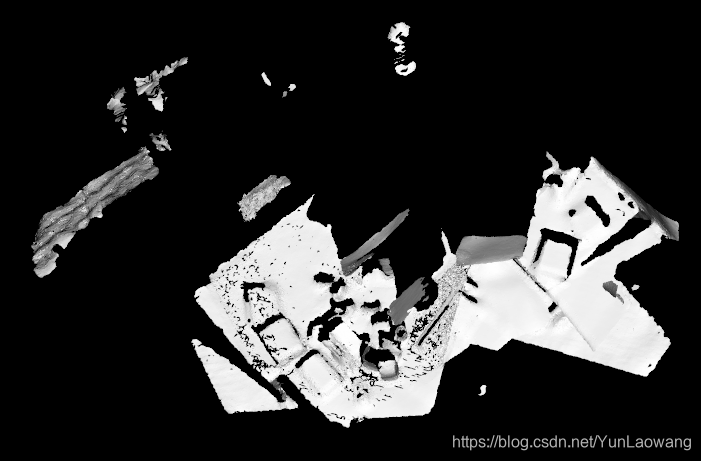

- 备注:
所需点云源文件【公众号提供】:h?ttps://pan?.baidu.com/s/1avSGdi4IG3ry3wNCI_jDLQ 提?取?码:cxjy(删除"?"即可访问)