Human visual system(HVS)
Mechanisms of Visual Attention in The Human Cortex
(Annual Review of Neuroscience 2003)
1. Competition among multiple stimuli
Evidence indicates that, first, there is competition among multiple stimuli for representation in visual cortex (神经皮质).
- Thus,multiple stimuli presented at the same time are not processed independently but rather interact with each other in a mutually suppressive (相互压制) way.
2. Different mechanisms
Second, competition among multiple stimulican be biased by both bottom-up, sensory-driven mechanisms (自下而上的感官驱动机制) and top-down feed-back (自上而下的反馈机制) mechanisms.
Selective Attention :
-
the enhancement of neural responses to attended stimuli;
对关注刺激信号的神经反应的增强;
-
the filtering of unwanted information by counteracting the suppression induced by nearby distracters;
通过抵消附近干扰因素引起的抑制来过滤不需要的信息;
-
the biasing of signals in favor of an attended location by increases of baseline activity in the absence of visual stimulation;
在没有视觉刺激的情况下, 改变激活脑区会影响未来信号的竞争优势;
Thus,stimuli at attended locations are biased to “win” the competition for processingresources.
-
the increase of stimulus salience by enhancing the neuron’s sensitivity to stimulus contrast.
通过提高神经元对刺激对比度的敏感性来增加刺激显着性。
总结来说,Selective Attention 有4种实现方式:
-
bottom-up: 增强关注刺激 / 削弱无关刺激
-
top-down: 基线移位 / 强化对比度敏感性
视觉皮层中活动的注意调节也可以在没有视觉刺激的情况下发生。
3. Where does top-down biasing signals from?
although competition is ultimately resolved within visual cortex, the source of top-down biasing signals derives from a network of areas outside visual cortex.
4. Signal for guiding
Fourth, and finally, the stimulus that wins the competition for representation in visual cortex will gain further access to memory systems for mnemonic encoding and retrieval and to motor systems for guiding action and behavior.
*. HVS 中 Attention 的本质
提供用于 信号间竞争 的处理策略。
Attention
Attention 注意力,起源于Human visual system(HVS), 外界给一个刺激Stimuli,HVS会第一时间产生对应的 saliency map,attention 对应的就是这个显著性区域。
总的来说,Attention 就是 区域权值学习 问题:
- Hard-attention,就是0/1问题,哪些区域是被 attentioned,哪些区域不关注
- Soft-attention,[0,1]间连续分布问题,每个区域被关注的程度高低,用0~1的score表示
- Self-attention,就是 feature map 间的自主学习,分配权重(可以是 spatial,可以是 temporal,也可以是 channel间)
SE-Net (channel attention)

-
Squeeze 操作,我们顺着空间维度来进行特征压缩,将每个二维的特征通道变成一个实数,这个实数某种程度上具有全局的感受野,并且输出的维度和输入的特征通道数相匹配。它表征着在特征通道上响应的全局分布,而且使得靠近输入的层也可以获得全局的感受野,这一点在很多任务中都是非常有用的。
实现上,即将输入特征进行 Global AVE pooling,得到 1* 1* Channel
-
Excitation 操作,它是一个类似于循环神经网络中门的机制。通过参数 w 来为每个特征通道生成权重,其中参数 w 被学习用来显式地建模特征通道间的相关性。
-
Reweight 的操作,我们将 Excitation 的输出的权重看做是进过特征选择后的每个特征通道的重要性,然后通过乘法逐通道加权到先前的特征上,完成在通道维度上的对原始特征的重标定。
CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module ECCV 2018(+spatial attention)
channel-wise attention 看成是教网络 Look 'what’;而spatial attention 看成是教网络 Look ‘where’
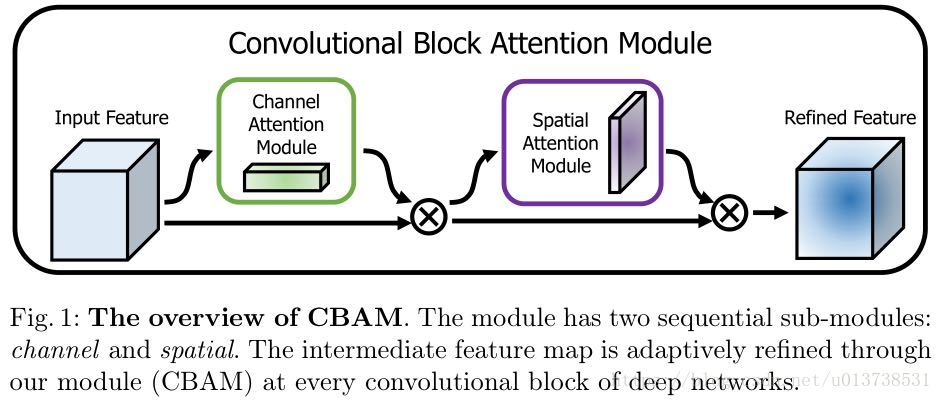
Spatial attention module
与channel attention不同,spatial attention主要关注于位置信息(where)。
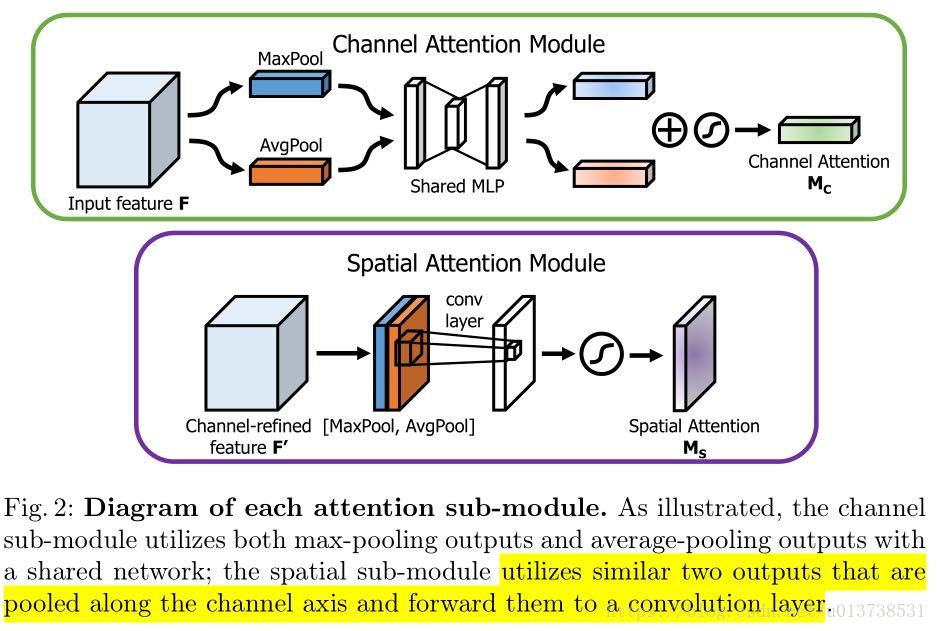
对输入特征进行 channel 间的 AVE 和 Max pooling,然后 concatenation,再来个7*7大卷积,最后 Sigmoid
DANet, CVPR2019 (channel & spatial attention)
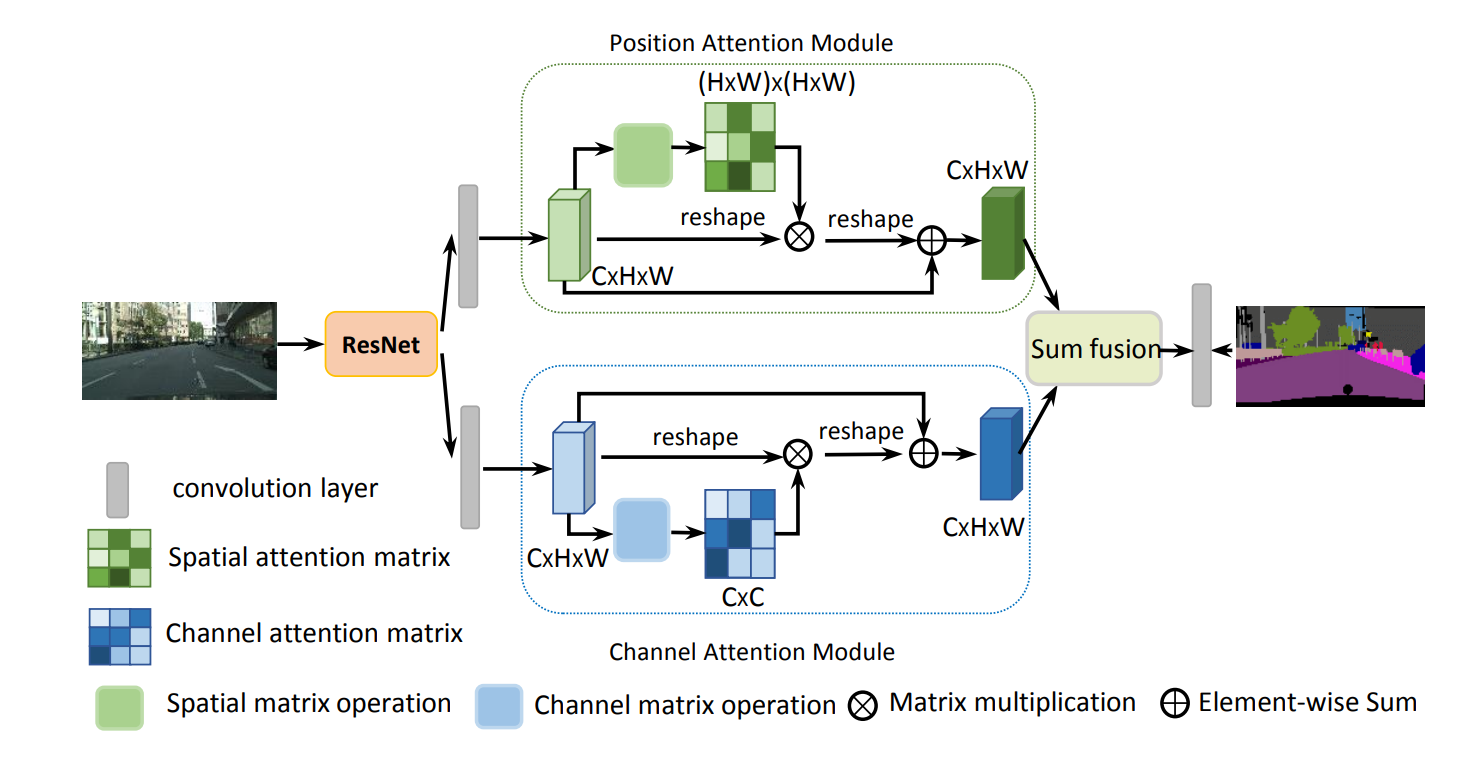
把Self-attention的思想用在图像分割,可通过long-range上下文关系更好地做到精准分割。
把deep feature map进行spatial-wise self-attention,同时也进行channel-wise self-attetnion,最后将两个结果进行 element-wise sum 融合。
参考链接:
SE-Net:https://www.jianshu.com/p/7244f64250a8
CBAM:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21612131/article/details/83217371
太过久远了,还有一些参考链接已经找不到了,sry
希望有点有用的东西