本节内容
1、IDLE的替代工具
2、数字、字符串、对象
3、注释
4、用户输入
5、python的内置数据结构
5、创建列表
6、列表的特性
7、总结与习题
一、pycharm and jupyter notebook
思考:
1、甚么是IDE?

1 ''' 2 集成开发环境(IDE,Integrated Development Environment )是用于提供程序开发环境的应用程序,一般包括代码编辑器、编译器、调试器和图形用户界面等工具。集成了代码编写功能、分析功能、编译功能、调试功能等一体化的开发软件服务套。 3 '''
2、甚么是IDLE?

1 #IDLE 是一个纯 Python 下自带的简洁的集成开发环境(IDE)
1、pycharm
安装网址:https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/ 安装过程(略)
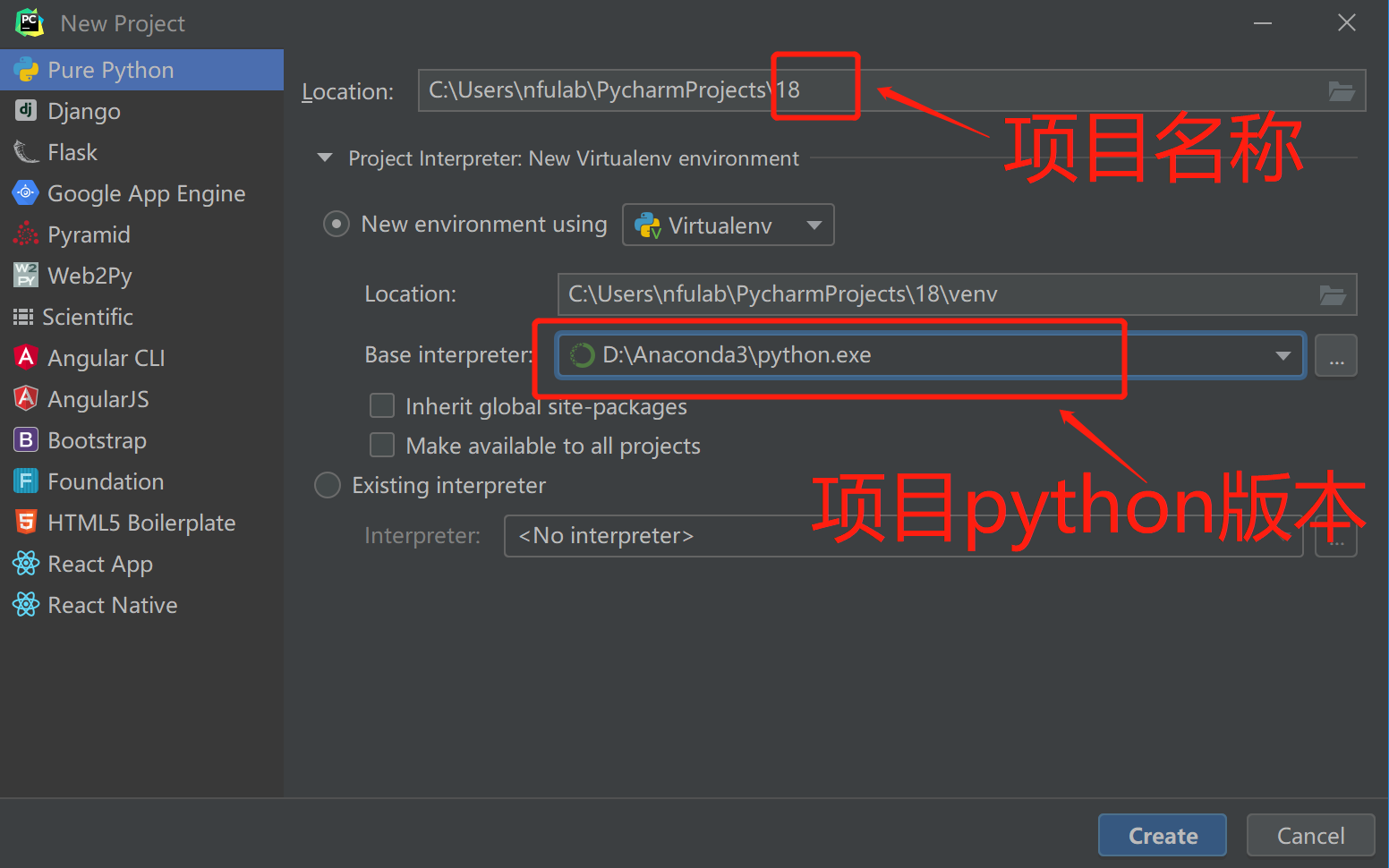
优势:1、可以自动补全。
2、方便于代码调试,可以随时终止进程。(vim、sublime等不能直接调试)
2、jupyter notebook
问题1:甚么是jupyter notebook?
问题2:如何在CMD中运行jupyter notebook?

尝试一下吧:
甚么是jupyter notebook?
1、jupyter是一个基于web的IDE(集成开发环境)。
2、兼具脚本操作和交互式操作的特性;
3、笔记式编辑代码和运行,便于调试,便于保存。
notebook使用举例:
主要为开发商和数据科学家提供举办机器学习竞赛、托管数据库、编写和分享代码的平台。
Inside Kaggle you’ll find all the code & data you need to do your data science work. Use over 19,000 public datasets and 200,000 public notebooks to conquer any analysis in no time.
eg:
2、 在cmd中运行jupyter:
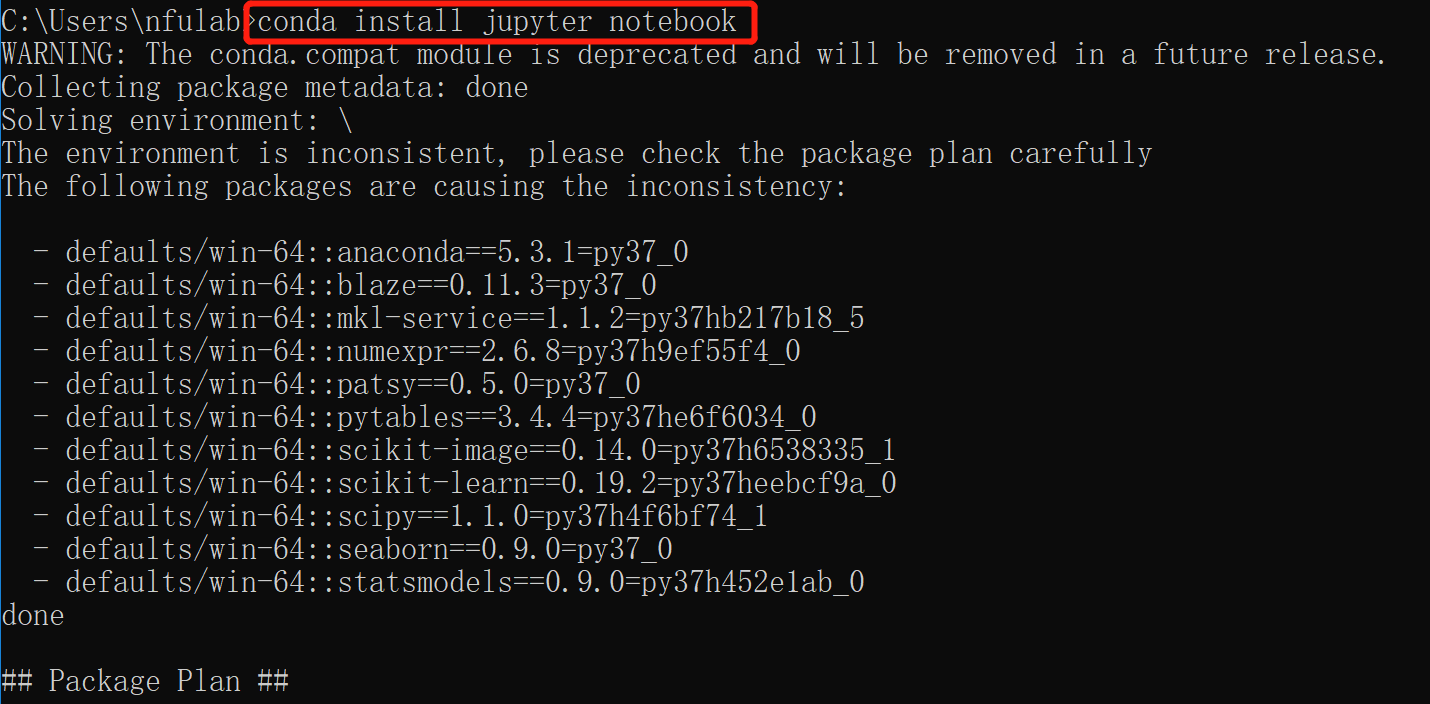
①安装
②运行
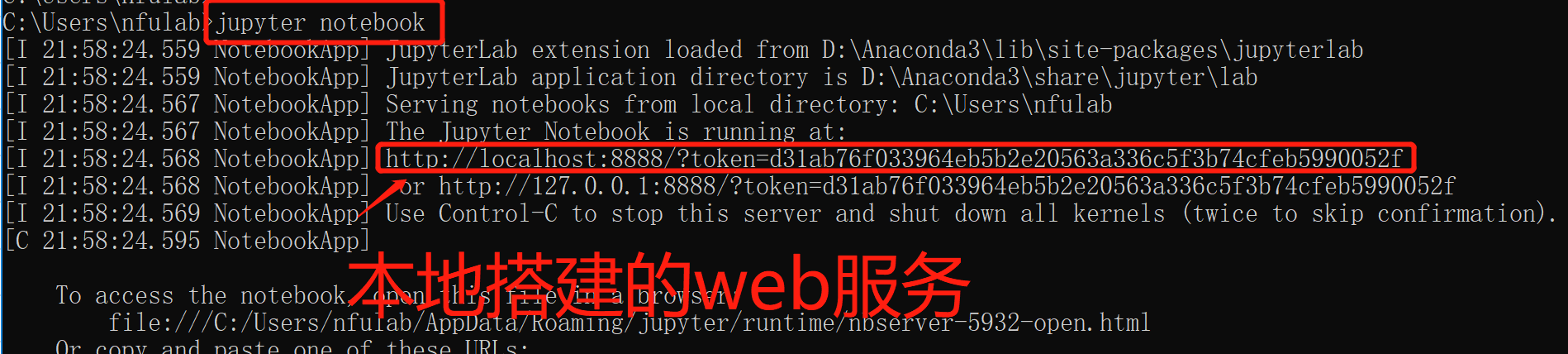
学会了么?是不是很简单。
总结:
cmd/IDLE 中的交互执行:偶尔执行一些简单的语句、测试
jupyter notebook:介于交互和脚本之间的(可做笔记,关心中间过程的输出)
IDLE 小型项目,学习初期的选择,功能完善
PyCharm 中大型项目中方便组织较多文件,功能更为丰富
pycharm 将成为学习python之路上的最重要的工具。
jupyter 将成为我们数据科学(包含大数据、数据分析)之路的重要工具。
二、变量(数字、字符串、对象)
请同学们一定要详细阅读:https://docs.python.org/3.7/tutorial/introduction.html#numbers 学有余力的同学将链接中的代码学习一遍。
1、数字(Numbers)
The integer numbers (e.g. 2, 4, 20) have type int, the ones with a fractional part (e.g. 5.0, 1.6) have type float. We will see more about numeric types later in the tutorial.
1 >>> 2 + 2 2 4 3 >>> 50 - 5*6 4 20 5 >>> (50 - 5*6) / 4 6 5.0 7 >>> 8 / 5 # division always returns a floating point number 8 1.6
Division (/) always returns a float. To do floor division and get an integer result (discarding any fractional result) you can use the // operator; to calculate the remainder you can use %:
1 >>> 17 / 3 # classic division returns a float 2 5.666666666666667 3 >>> 4 >>> 17 // 3 # floor division discards the fractional part 5 5 6 >>> 17 % 3 # the % operator returns the remainder of the division 7 2 8 >>> 5 * 3 + 2 # result * divisor + remainder 9 17
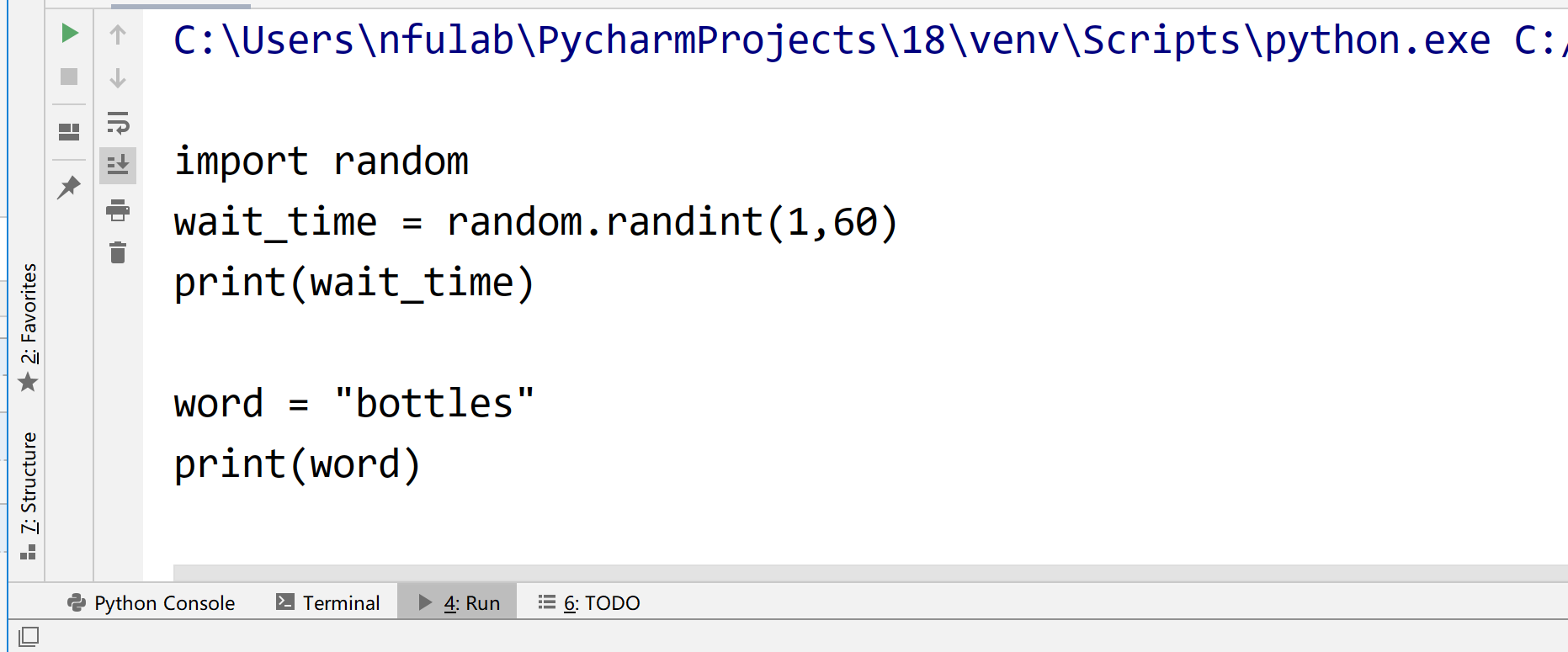
1 import random 2 wait_time = random.randint(1,60) 3 print(wait_time)
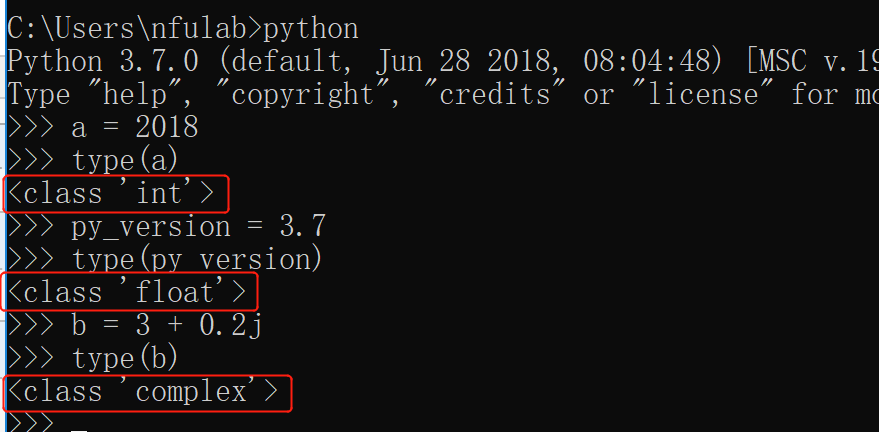
Python中的数据类型(整型、浮点型和 复数 )
eg:
2、字符串(Strings)
Besides numbers, Python can also manipulate strings, which can be expressed in several ways.
They can be enclosed in single quotes ('...') or double quotes ("...") with the same result 2. \ can be used to escape quotes
1 >>> 'spam eggs' # single quotes 2 'spam eggs' 3 >>> 'doesn\'t' # use \' to escape the single quote... 4 "doesn't" 5 >>> "doesn't" # ...or use double quotes instead 6 "doesn't" 7 >>> '"Yes," they said.' 8 '"Yes," they said.' 9 >>> "\"Yes,\" they said." 10 '"Yes," they said.' 11 >>> '"Isn\'t," they said.' 12 '"Isn\'t," they said.'
3、对象
python中“一切皆是对象”。P48-49 了解
三、注释
单行注释:# 被注释内容
eg1:
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 # Author:Zhichao
多行注释:""" 被注释内容 """
eg2:
1 ''' 2 import random 3 wait_time = random.randint(1,60) 4 print(wait_time) 5 6 word = "bottles" 7 print(word) 8 '''
除此之外,""" 被注释内容 """ 还可以打印变量
eg:3
1 test1 =''' 2 import random 3 wait_time = random.randint(1,60) 4 print(wait_time) 5 6 word = "bottles" 7 print(word) 8 ''' 9 print(test1)
4、用户输入
eg:
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 # Author:Zhichao 3 4 username = input("username:") 5 password = input("password:") 6 7 print(username,password)

字符串拼接+打印:
eg:
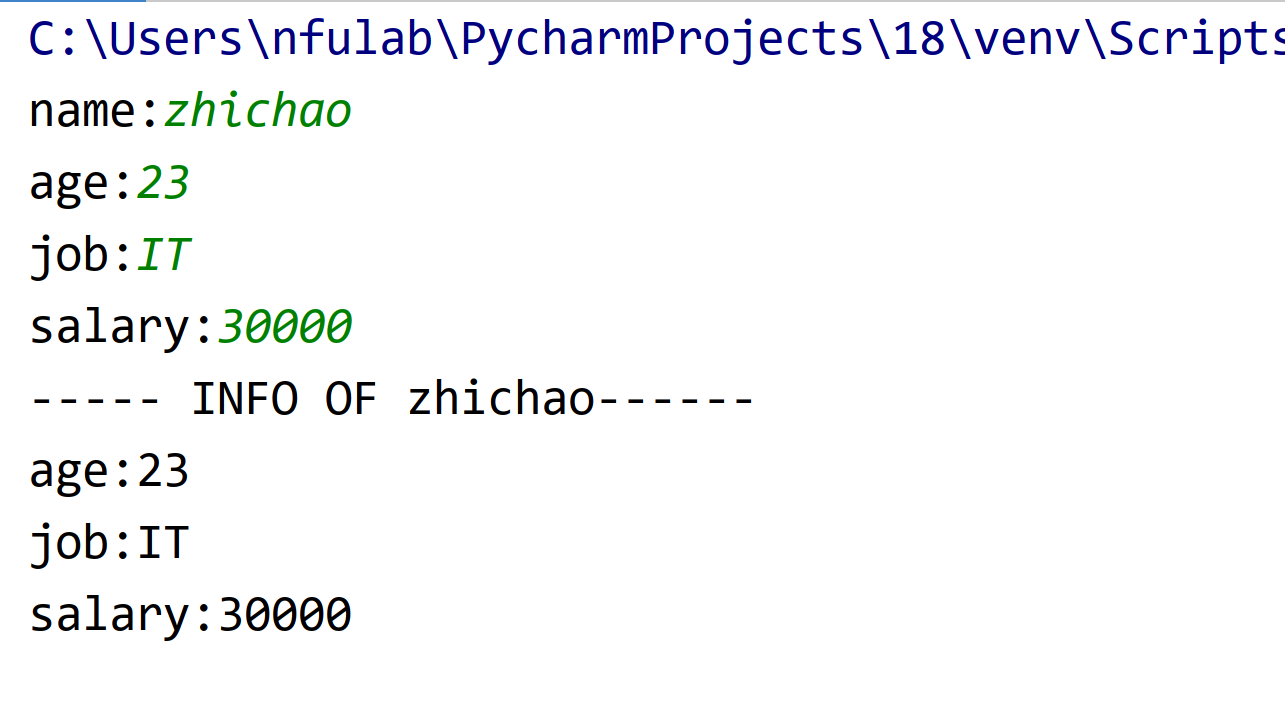
1 name = input("name:") 2 age = input("age:") 3 job = input("job:") 4 salary = input("salary:") 5 6 info = '''----- INFO OF ''' + name +'''------''' + ''' 7 age:''' + age+''' 8 job:''' + job +''' 9 salary:'''+salary 10 11 print(info)
是不是很麻烦?有没有更简单的方式将打印内容?接下来我们来学习 %s 占位符。
1 name = input("name:") 2 age = input("age:") 3 job = input("job:") 4 salary = input("salary:") 5 6 info = '''-------INFO OF %s ------- 7 Name:%s 8 Age:%s 9 Job:%s 10 Salary:%s 11 '''% (name,name,age,job,salary) 12 13 print(info)
%s代表 string
%d代表 number
%f代表 float
更进一步:设置数据类型,将age、salary设置为number。

1 name = input("name:") 2 age = int(input("age:")) #注意! python中默认所有的输入均为string 3 job = input("job:") 4 salary = int(input("salary:")) 5 6 info = '''-------INFO OF %s ------- 7 Name:%s 8 Age:%d 9 Job:%s 10 Salary:%d 11 '''% (name,name,age,job,salary) 12 13 print(info)
.format():

1 info2 = '''-------INFO OF {_name} ------- 2 Name:{_name} 3 Age:{_age} 4 Job:{_job} 5 Salary:{_salary} 6 '''.format(_name=name, 7 _age=age, 8 _job=job, 9 _salary=salary) 10 print(info2)

1 info3 = '''-------INFO OF {0} ------- 2 Name:{0} 3 Age:{1} 4 Job:{2} 5 Salary:{3} 6 '''.format(name,age,job,salary) 7 print(info3)
