6.1 vector的常见用法详解
vector:变长数组,长度根据需要而自动改变的数组
要使用vector,则需要添加vector头文件,即#include<vector>,还需要在头文件下面加上一句“using namespace std;”
1.vector的定义
单独定义一个vector
vector<typename> name;
typename可以是任何基本类型,例如int,double,char,结构体等,也可以是STL标准容器,例如vector、set、queue等。
如果typename也是一个STL容器,定义的时候要记得在>>符号之间加上空格。
vector数组的定义方法:vector<typename> Arrayname[arraySize];
这样Arrayname[0]~Arrayname[arraySize-1]中每一个都是一个vector容器。
2.vector容器内元素的访问
(1)通过下标访问
vector<typename> vi;
vi[index]
下标是从0到vi.size()-1
(2)通过迭代器访问
vector<typename>::iterator it:
举例:
vector<int>::iterator it;
vector<double>::iterator it;
#include<cstdio> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main(){ vector<int> vi; for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){ vi.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator it = vi.begin(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ printf("%d ",*(it+i)); } return 0; }
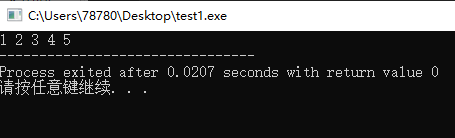
vi[i]和*(vi.begin()+i)是等价的
迭代器还实现了两种自加操作:++it 和 it++
#include<cstdio> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main(){ vector<int> vi; for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){ vi.push_back(i); } for(vector<int>::iterator it = vi.begin();it!=vi.end();it++){ printf("%d ",*it); } return 0; }
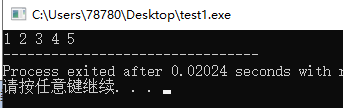
只有vector和string中,才允许使用vi.begin()+3这种迭代器加上整数的写法。
3.vector常用函数实例解析
(1)push_back(x):在vector后面添加一个元素x,时间复杂度为O(1)
(2)pop_back():删除vector的尾元素,时间复杂度为O(1)
(3)size():获得vector中元素的个数,时间复杂度为O(1)
(4)clear():清空vector中的所有元素,时间复杂度为O(N),N为vector中元素的个数
(5)insert():insert(i,x)用来向vector的任意迭代器it处插入一个元素x,时间复杂度O(N)
(6)erase()有两种用法:删除单个元素、删除一个区间内的所有元素。
1、删除单个元素 vi.erase(vi.begin()+3); 删除vi[3]
2、删除一个区间内的所有元素:vi.erase(vi.begin()+1,vi.begin()+4); 删除vi[1]、vi[2]、vi[3]
4.vector的常见用途
(1)储存数据
(2)用邻接表存储图
PAT A1039 Course List for Student
Zhejiang University has 40000 students and provides 2500 courses. Now given the student name lists of all the courses, you are supposed to output the registered course list for each student who comes for a query.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 2 positive integers: N (≤), the number of students who look for their course lists, and K (≤), the total number of courses. Then the student name lists are given for the courses (numbered from 1 to K) in the following format: for each course i, first the course index i and the number of registered students Ni (≤) are given in a line. Then in the next line, Ni student names are given. A student name consists of 3 capital English letters plus a one-digit number. Finally the last line contains the N names of students who come for a query. All the names and numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in N lines. Each line corresponds to one student, in the following format: first print the student's name, then the total number of registered courses of that student, and finally the indices of the courses in increasing order. The query results must be printed in the same order as input. All the data in a line must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
11 5
4 7
BOB5 DON2 FRA8 JAY9 KAT3 LOR6 ZOE1
1 4
ANN0 BOB5 JAY9 LOR6
2 7
ANN0 BOB5 FRA8 JAY9 JOE4 KAT3 LOR6
3 1
BOB5
5 9
AMY7 ANN0 BOB5 DON2 FRA8 JAY9 KAT3 LOR6 ZOE1
ZOE1 ANN0 BOB5 JOE4 JAY9 FRA8 DON2 AMY7 KAT3 LOR6 NON9
Sample Output:
ZOE1 2 4 5
ANN0 3 1 2 5
BOB5 5 1 2 3 4 5
JOE4 1 2
JAY9 4 1 2 4 5
FRA8 3 2 4 5
DON2 2 4 5
AMY7 1 5
KAT3 3 2 4 5
LOR6 4 1 2 4 5
NON9 0#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 40010; const int M = 26*26*26*10+1; vector<int> selectCourse[M]; int getID(char name[]){ int id = 0; for(int i = 0;i<3;i++){ id = id * 26 + (name[i] - 'A'); } id = id * 10 + (name[3] - '0'); return id; } int main(){ char name[5]; int n,k; scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ int course,x; scanf("%d%d",&course,&x); for(int j = 0;j<x;j++){ scanf("%s",name); int id = getID(name); selectCourse[id].push_back(course); } } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%s",name); int id = getID(name); sort(selectCourse[id].begin(),selectCourse[id].end()); printf("%s %d",name,selectCourse[id].size()); for(int j=0;j<selectCourse[id].size();j++){ printf(" %d",selectCourse[id][j]); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }