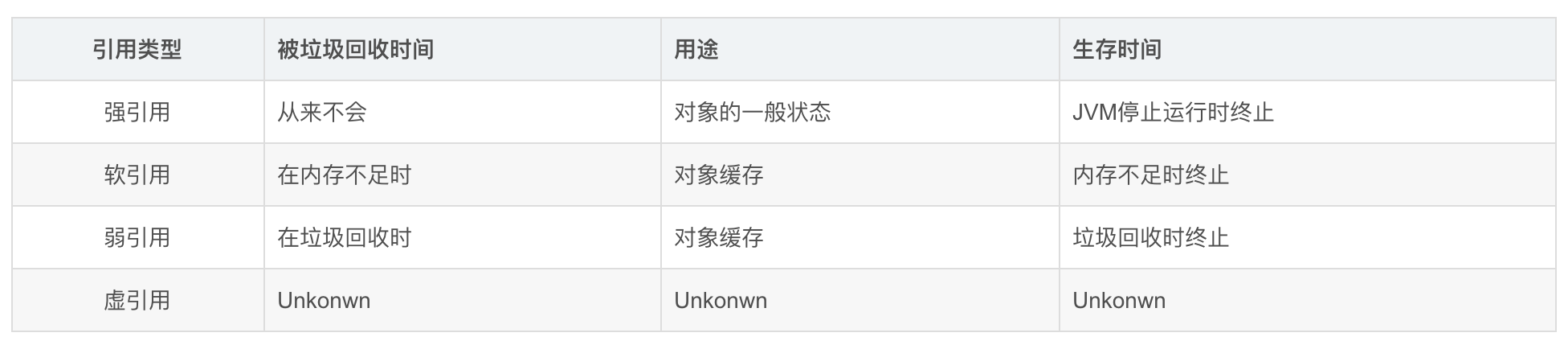
1.首先我们要知道jvm 对于对象的管理分为四种
强引用
软引用
弱引用
虚引用
偷来的图片 :
2. 既然在两次 gc 之间 弱引用可以进行存活,那么我们就可以实现缓存
代码
java 令人头疼的设计模式
package com.jvm.chop03.cache;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Cache {
private static Cache cache;
private ReferenceQueue<Man> queue;
private ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ManRef> cacheTabel;
private static Object lock;
//单例
private Cache() {
queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
cacheTabel = (ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ManRef>) Collections.synchronizedMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ManRef>());
}
public static Cache getInstance(){
if(cache == null){
synchronized (lock){
if(cache == null){
cache = new Cache();
}
}
}
return cache;
}
private static class ManRef extends SoftReference<Man> {
private int id;
public ManRef(Man man, ReferenceQueue queue) {
super(man, queue);
id = man.getId();
}
}
public synchronized void into(Man man){
clear();
ManRef manRef = new ManRef(man, queue);
cacheTabel.put(man.getId(),manRef);
}
private void clear() {
ManRef ref ;
while((ref = (ManRef) queue.poll())==null){
int id= ref.id;
cacheTabel.remove(id);
}
}
public Man getMen(Integer id){
if(cacheTabel.contains(id)){
return cacheTabel.get(id).get();
}else{
// Man man = getFromDB(id);
// into(man);
// return man;
return null;
}
}
}解读 : 单例 双判断加锁 ,接口实现 两个get put ,对于所有的对象使用弱引用 存储于 hashmap
获取时候新进行清除,在进行获取