之前我们做的是将所有的配置信息几乎都写在了applicationContext.xml配置文件中了,这样,这个配置文件势必会变得非常的庞大,不利于后期的维护。
现在,我们需要对这个配置文件进行拆分。
现在我先按照层次进行拆分
applicationContext-dao.xml
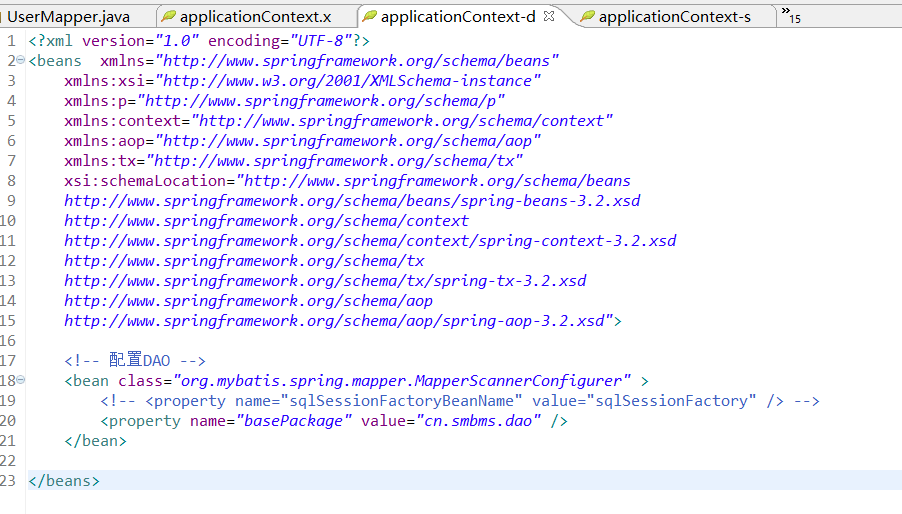
applicationContext-service.xml
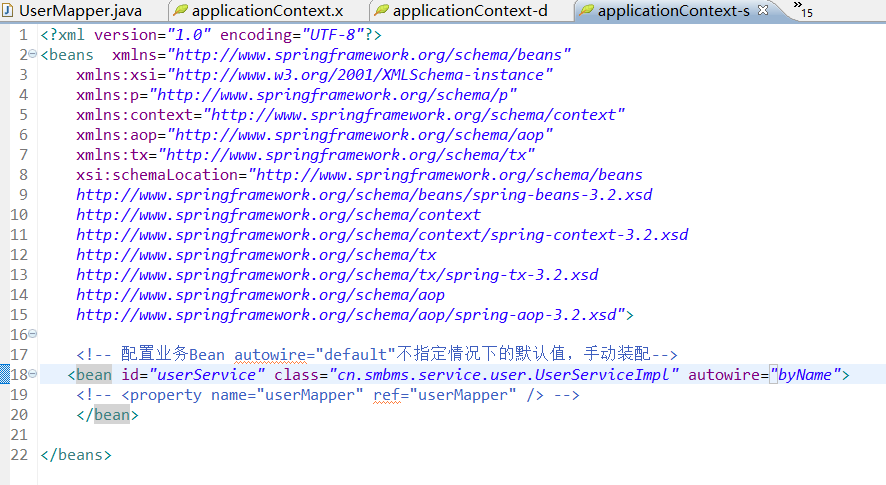
applicationContext.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
5 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
6 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
7 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
8 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
14 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
15 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd">
16
17 <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer" >
18 <property name="location">
19 <value>classpath:database.properties</value>
20 </property>
21 </bean>
22 <!-- 配置DataSource -->
23 <!-- <bean id="dataSource" destroy-method="close" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" autowire="no">
24 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
25 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
26 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
27 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
28 </bean> -->
29
30 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean" >
31 <property name="jndiName">
32 <value>java:comp/env/jndi/smbms</value>
33 </property>
34 </bean>
35
36 <!-- 配置SqlSessionFactoryBean -->
37 <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean" >
38 <!-- 引用数据源组件 -->
39 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
40 <!-- 引用MyBatis配置文件中的配置 -->
41 <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" />
42 </bean>
43
44
45 <!-- <context:component-scan base-package="cn.smbms.service" /> -->
46 <!-- 定义事务管理器 -->
47 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
48 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
49 </bean>
50 <tx:annotation-driven />
51 <!-- <tx:advice id="txAdvice">
52 <tx:attributes>
53 <tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" />
54 <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
55 <tx:method name="del*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
56 <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
57 <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
58 </tx:attributes>
59 </tx:advice> -->
60 <!-- 定义切面 -->
61 <!-- <aop:config>
62 <aop:pointcut id="serviceMethod"
63 expression="execution(* cn.smbms.service..*.*(..))" />
64 <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="serviceMethod" />
65 </aop:config> -->
66 </beans>
进行配置文件的组装,有两种方法
第一种:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String...);不定长参数
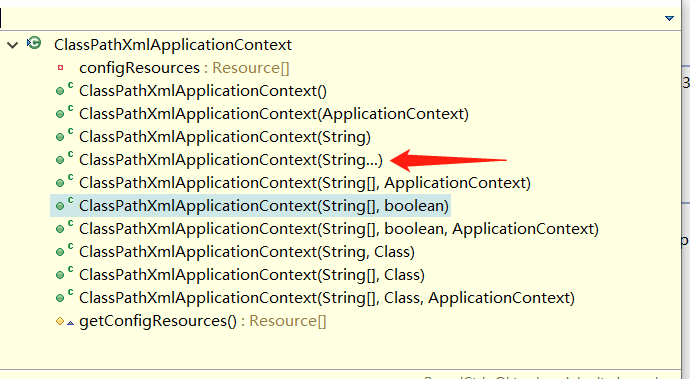
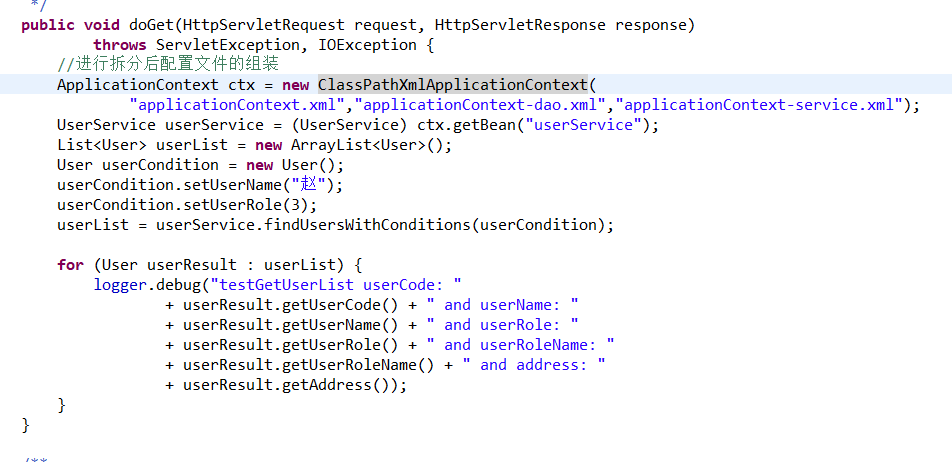
第二种方式使用import标签元素进行导入,这种方式我个人觉得比较友好。
在applicationContext.xml中进行如下配置,非常简单
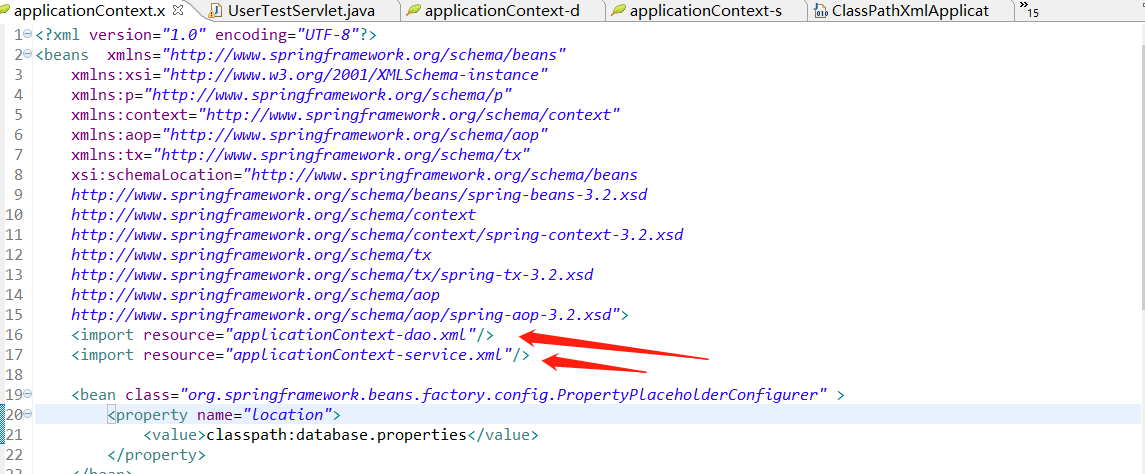
运行结果:
