1、介绍。
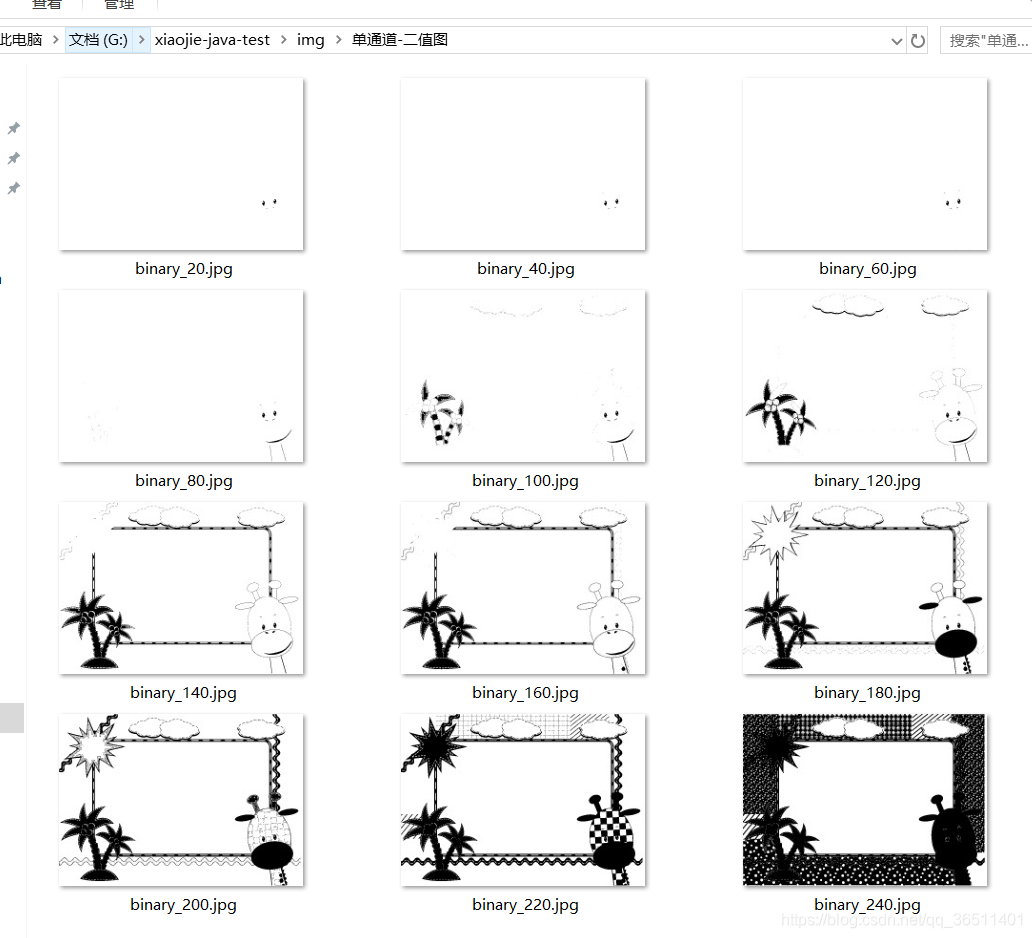
二值化。图像二值化( Image Binarization)就是将图像上的像素点的灰度值设置为0或255,也就是将整个图像呈现出明显的黑白效果的过程。在数字图像处理中,二值图像占有非常重要的地位,图像的二值化使图像中数据量大为减少,从而能凸显出目标的轮廓。
图像通道。在Photoshop中有一个很重要概念叫图像通道,在RGB色彩模式下就是指那单独的红色、绿色、蓝色部分。也就是说,一幅完整的图像,是由红色绿色蓝色三个通道组成的。他们共同作用产生了完整的图像。
下面我会介绍这7种方法,以下图所示的源图为例。

2、代码
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
public class ImgTest {
private static final byte Gray_Type_Min = 1;//最大值法
private static final byte Gray_Type_Max = 2;//最小值法
private static final byte Gray_Type_Average = 3;//平均值法
private static final byte Gray_Type_Weight = 4;//加权法
private static final byte Gray_Type_Red = 5;//红色值法
private static final byte Gray_Type_Green = 6;//绿色值法
private static final byte Gray_Type_Blue = 7;//蓝色值法
private static final String File_Path = "G:\\xiaojie-java-test\\img\\%s\\%s.jpg";
private static final String Source_Path = "G:\\xiaojie-java-test\\img\\source.jpg";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取不同通道图片的方法
toChannelImg();
//先灰度化,再二值化(灰度化暂时使用加权法)
toBinaryImg(20);
toBinaryImg(40);
toBinaryImg(60);
toBinaryImg(80);
toBinaryImg(100);
toBinaryImg(120);
toBinaryImg(140);
toBinaryImg(160);
toBinaryImg(180);
toBinaryImg(200);
toBinaryImg(220);
toBinaryImg(240);
}
/**
* 获取不同通道图片的方法
*/
private static void toChannelImg() {
try {
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(new File(Source_Path));
final int imgWidth = image.getWidth();
final int imgHeight = image.getHeight();
BufferedImage bufferedImage_red = new BufferedImage(imgWidth, imgHeight, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
BufferedImage bufferedImage_green = new BufferedImage(imgWidth, imgHeight, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
BufferedImage bufferedImage_blue = new BufferedImage(imgWidth, imgHeight, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
//这边因为只是灰度操作,所以内外循环imgWidth和imgHeight可以随便放
for (int i = 0; i < imgHeight; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < imgWidth; j++) {
final int pixel = image.getRGB(j, i);
bufferedImage_red.setRGB(j, i, pixel & 0xff0000);
bufferedImage_green.setRGB(j, i, pixel & 0x00ff00);
bufferedImage_blue.setRGB(j, i, pixel & 0x0000ff);
//System.out.print(String.format("%4d ", gray));
}
//System.out.println();
}
ImageIO.write(bufferedImage_red, "JPEG", new File(String.format(File_Path, "三通道-图像通道", "red")));
Thread.sleep(1);
ImageIO.write(bufferedImage_green, "JPEG", new File(String.format(File_Path, "三通道-图像通道", "green")));
Thread.sleep(1);
ImageIO.write(bufferedImage_blue, "JPEG", new File(String.format(File_Path, "三通道-图像通道", "blue")));
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//先灰度化,再二值化(灰度化暂时使用加权法)
private static void toBinaryImg(int threshold) {
try {
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(new File(Source_Path));
final int imgWidth = image.getWidth();
final int imgHeight = image.getHeight();
BufferedImage bufferedImage = new BufferedImage(imgWidth, imgHeight, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_BINARY);
//这边因为只是灰度操作,所以内外循环imgWidth和imgHeight可以随便放
for (int i = 0; i < imgHeight; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < imgWidth; j++) {
final int pixel = image.getRGB(j, i);
final int[] grb = getRgb(pixel);
final int gray = getGray(grb, Gray_Type_Weight);
bufferedImage.setRGB(j, i, (byte) (gray < threshold ? 0 : 255));
//System.out.print(String.format("%4d ", gray));
}
//System.out.println();
}
ImageIO.write(bufferedImage, "JPEG", new File(String.format(File_Path, "单通道-二值图", "binary_" + threshold)));
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//将一个int值转化为3个r、g个b的byte值
private static int[] getRgb(int pixel) {
int[] rgb = new int[3];
rgb[0] = (pixel >> 16) & 0xff;
rgb[1] = (pixel >> 8) & 0xff;
rgb[2] = pixel & 0xff;
return rgb;
}
//根据不同的灰度化方法,返回byte灰度值
private static int getGray(int[] rgb, int type) {
if (type == Gray_Type_Average) {
return (rgb[0] + rgb[1] + rgb[2]) / 3; //rgb之和除以3
} else if (type == Gray_Type_Weight) {
return (int) (0.3 * rgb[0] + 0.59 * rgb[1] + 0.11 * rgb[2]);
} else if (type == Gray_Type_Red) {
return rgb[0];//取红色值
} else if (type == Gray_Type_Green) {
return rgb[1];//取绿色值
} else if (type == Gray_Type_Blue) {
return rgb[2];//取蓝色值
}
//比较三个数的大小
int gray = rgb[0];
for (int i = 1; i < rgb.length; i++) {
if (type == Gray_Type_Min) {
if (gray > rgb[i]) {
gray = rgb[i];//取最小值
}
} else if (type == Gray_Type_Max) {
if (gray < rgb[i]) {
gray = rgb[i];//取最大值
}
}
}
return gray;
}
}3、结果。