个别关键字的使用
//1.在c语言中typedef的使用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef unsigned int unit ;
int main(){
unsigned int num2 = 10;
//给 unsigned int 另起的别名叫unit
unit num1 = 5;
int sum = num1 + num2;
printf("%d\n", sum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.在c语言中 static用来修饰变量和函数的
1.修饰局部变量(修改了生命周期就变成整个程序了)
2.修饰全局变量(修改了变量的作用域,只能在当前作用域中访问,不能跨文件访问)
3.修饰一个函数和修饰全局变量是一样的,修改了作用域为当前文件中访问。
//2.观察调用几次结果如何改变
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Fun(){
int i = 1;
i = i + 1;
printf("%d\n", i);
}
int main(){
Fun();
Fun();
Fun();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

//3.const 定义常量
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int a = 10;
printf("%d\n", a);
a = 20;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//对变量进行了修改
运行结果:

#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
const int a = 10;//利用了const对常量进行定义
printf("%d\n", a);
a = 20;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//利用了const 对a进行了定义,此时a已经时常量无法发生修改。
运行结果:
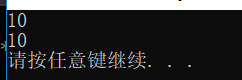
//4. #define 来定义常量
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define A 10
int main(){
printf("%d\n", A);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//常量均不能修改**,因为此时常量的大小已经确定
运行结果:

