设计模式:OOP语言开发过程中,遇到种种场景和问题,提出的解决方案
-----设计模式,其实就是解决问题的套路
1.设计模式包含三种类型:
创造型设计模式:
关注对性的创建--三大工厂+创造者+单例+原型
即使是一个简单的对象复用,都有很多招数
结构型设计模式
行为型设计模式
2.单例模式:保证整个进程中,该对象只有一个实例
/// <summary>
/// 单例类
/// </summary>
public class StudentSington
{
/// <summary>
/// 1.构造器函数私有化--避免随意构造
/// </summary>
private StudentSington()
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
long lReasult = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
lReasult += i;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}被构造.", this.GetType().Name);
}
/// <summary>
/// 2.私有的静态字段--内存唯一,不会释放,在第一次使用这个类时被初始化,且只初始化一次
/// </summary>
private static StudentSington studentSington = new StudentSington() { Id = 1, Name = "StudentA" };
/// <summary>
/// 3.公开的静态方法来提供实例
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static StudentSington GetInstance()
{
if (studentSington != null)
return studentSington;
else
{
studentSington = new StudentSington() { Id = 1, Name = "StudentA" };
return studentSington;
}
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Study()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.Name}正在学习,请勿扰");
}
}
测试:
//不同的方法/类/线程/类库的重用? ---单例模式:保证整个进程中,该对象只有一个实例
//单例在整个进程中只有一个实例--不能出来呢2个学生,--如果两个学生都写个了某个属性,后一个会覆盖前一个
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
StudentSington student = StudentSington.GetInstance();
student.Study();
}
Console.ReadLine();
3.原型模式:利用对象Copy,快速获取对象。需要大量的新对象的时候可以用原型模式
/// <summary>
/// 原型模式
/// </summary>
public class StudentPrototype
{
/// <summary>
/// 1.构造器函数私有化--避免随意构造
/// </summary>
private StudentPrototype()
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
long lReasult = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
lReasult += i;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}被构造.", this.GetType().Name);
}
/// <summary>
/// 2.私有的静态字段--内存唯一,不会释放,在第一次使用这个类时被初始化,且只初始化一次
/// </summary>
private static StudentPrototype student = new StudentPrototype() { Id = 1, Name = "StudentA", Class = new Class() { ClassId = 1, ClassName = ".net高级班" } };
/// <summary>
/// 3.公开的静态方法来提供实例
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
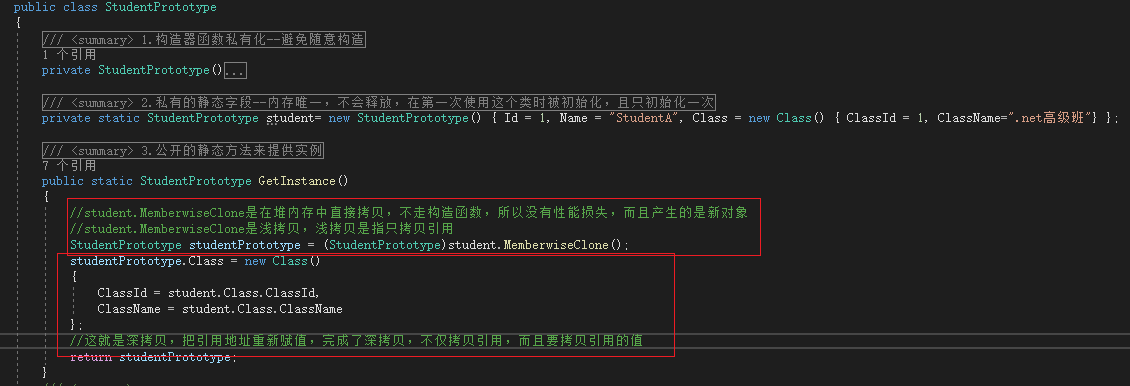
public static StudentPrototype GetInstance()
{
//student.MemberwiseClone是在堆内存中直接拷贝,不走构造函数,所以没有性能损失,而且产生的是新对象
//student.MemberwiseClone是浅拷贝,浅拷贝是指只拷贝引用
StudentPrototype studentPrototype = (StudentPrototype)student.MemberwiseClone();
return studentPrototype;
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Class Class { get; set; }
public void Study()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.Name}正在学习,请勿扰");
}
}
public class Class
{
public int ClassId { get; set; }
public string ClassName { get; set; }
}
测试代码:
//单例可以对象复用--但是会出现属性覆盖
//修改使其实现不覆盖,又可以复用对象,且性能高-->原型模式
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
StudentPrototype student = StudentPrototype.GetInstance();
student.Study();
}
StudentPrototype student1 = StudentPrototype.GetInstance();
student1.Name = "student1";
StudentPrototype student2 = StudentPrototype.GetInstance();
student2.Name = "student2";
student1.Study();
student2.Study();
Console.ReadLine();
4.深拷贝和浅拷贝
4.1)浅拷贝和深拷贝
4.2 深拷贝的三种方式:
4.2.1.直接New
4.2.2.子类提供原型方式
4.2.3.基于序列化反序列化:
4.2.3.1当前类和子类都要用序列化属性标记
4.2.3.2 调用深度克隆的序列化方法
/// <summary>
/// 原型模式
/// </summary>
public class StudentPrototype
{
/// <summary>
/// 1.构造器函数私有化--避免随意构造
/// </summary>
private StudentPrototype()
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
long lReasult = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
lReasult += i;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}被构造.", this.GetType().Name);
}
/// <summary>
/// 2.私有的静态字段--内存唯一,不会释放,在第一次使用这个类时被初始化,且只初始化一次
/// </summary>
private static StudentPrototype student = new StudentPrototype() { Id = 1, Name = "StudentA", Class = new Class() { ClassId = 1, ClassName = ".net" } };
/// <summary>
/// 3.公开的静态方法来提供实例
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static StudentPrototype DeepClone()
{
return SerializableHelper.DeepClone<StudentPrototype>(student);
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Class Class { get; set; }
public void Study()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.Name}正在学习,请勿扰");
}
}
public class Class
{
public int ClassId { get; set; }
public string ClassName { get; set; }
}
public class SerializableHelper
{
public static string Serializable(Object target)
{
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream())
{
new BinaryFormatter().Serialize(stream, target);
return Convert.ToBase64String(stream.ToArray());
}
}
public static T Deriallizable<T>(string target)
{
byte[] targetArray = Convert.FromBase64String(target);
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream())
{
return (T)(new BinaryFormatter().Deserialize(stream));
}
}
public static T DeepClone<T>(T t)
{
return Deriallizable<T>(Serializable(t));
}
}
5. c#的内存分派机制
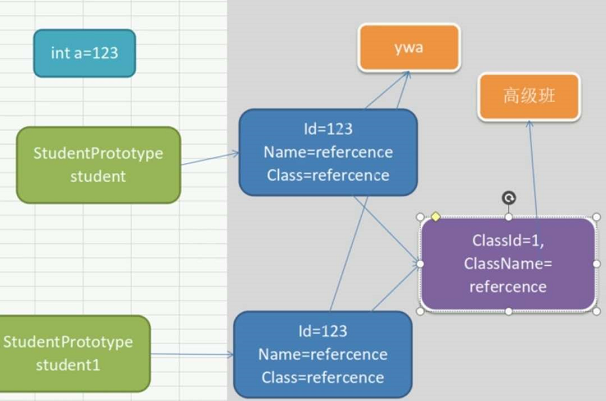
StudentPrototype student1 = StudentPrototype.GetInstance();
//student1.Name = "student1";等同于new String(""student1""),相当于开辟新空间,不会影响其他的,实际上string类型是不可修改的,所以当创建多个student之后,修改Name的值,都是互不影响的
2.1)c#内存分为:
进程堆(进程唯一.每个网站打开都有一个进程堆)
线程栈(每个线程一个)
引用类型在堆里,引用类型里面的值类型在堆里
值类型在栈中, 引用类型的变量和值类型的变量在栈中
值类型对应的引用类型--Custom.Name在堆里面(任何引用类型的值都在堆里面)
/// <summary>
/// 结构体是值类型,Custom.Name就是值类型中的引用类型
/// </summary>
public struct Custom
{
public string Name;
}
总结:
所有的引用类型的值一定在堆里面,
值类型如果是变量对应的值在栈里面,
如果是引用类型里面包裹的值类型,他的值在栈里面