计算属性
1、简单示例
<div id="app">
<p>最初信息:{{message}}</p>
<p>computed后信息:{{reversedMessage}}</p>
</div>
<script>
var app1=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello'
},
computed:{
reversedMessage:function(){
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('');
}
}
})
</script>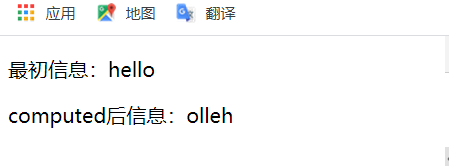
2、计算属性缓存vs方法
// 在组件中
methods: {
reversedMessage: function () {
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}将同一函数定义为一个方法而不是一个计算属性。两种方式的最终结果确实是完全相同的。然而,不同的是计算属性是基于它们的响应式依赖进行缓存的。只在相关响应式依赖发生改变时它们才会重新求值。这就意味着只要 message 还没有发生改变,多次访问 reversedMessage 计算属性会立即返回之前的计算结果,而不必再次执行函数。
为什么需要缓存?假设有一个性能开销比较大的计算属性 A,它需要遍历一个巨大的数组并做大量的计算。然后我们可能有其他的计算属性依赖于 A 。如果没有缓存,那么将不可避免的多次执行 A 的 getter!如果不希望有缓存,请用方法来替代。
3、计算属性vs侦听属性
Vue 提供了一种更通用的方式来观察和响应 Vue 实例上的数据变动:侦听属性。当你有一些数据需要随着其它数据变动而变动时,你很容易滥用 watch。
(1)watch回调
<div id="demo">{{ fullName }}</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar',
fullName: 'Foo Bar'
},
watch: {
firstName: function (val) {
this.fullName = val + ' ' + this.lastName
},
lastName: function (val) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + ' ' + val
}
}
})
</script>运行结果:Foo Bar
(2)计算属性
<div id="demo">{{ fullName }}</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar'
},
computed: {
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
}
}
})
</script>运行结果:Foo Bar
4、计算属性的setter
计算属性默认只有 getter ,不过在需要时你也可以提供一个 setter 。
<div id="demo">{{ fullName }}</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar'
},
computed: {
fullName: {
// getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
// setter
set: function (newValue) {
var names = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1]
}
}
}
})
</script>运行结果:Foo Bar
侦听器
虽然计算属性在大多数情况下更合适,但有时也需要一个自定义的侦听器。这就是为什么 Vue 通过 watch 选项提供了一个更通用的方法,来响应数据的变化。当需要在数据变化时执行异步或开销较大的操作时,这个方式是最有用的。
示例
<div id="watch-example">
<p>
Ask a yes/no question:
<input v-model="question">
</p>
<p>{{ answer }}</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script>
var watchExampleVM = new Vue({
el: '#watch-example',
data: {
question: '',
answer: 'I cannot give you an answer until you ask a question!'
},
watch: {
// 如果 `question` 发生改变,这个函数就会运行
question: function (newQuestion, oldQuestion) {
this.answer = 'Waiting for you to stop typing...'
this.debouncedGetAnswer()
}
},
created: function () {
this.debouncedGetAnswer = _.debounce(this.getAnswer, 500)
},
methods: {
getAnswer: function () {
if (this.question.indexOf('?') === -1) {
this.answer = 'Questions usually contain a question mark. ;-)'
return
}
this.answer = 'Thinking...'
var vm = this
axios.get('https://yesno.wtf/api')
.then(function (response) {
vm.answer = _.capitalize(response.data.answer)
})
.catch(function (error) {
vm.answer = 'Error! Could not reach the API. ' + error
})
}
}
})
</script>
