给定一个二叉树
struct Node { int val; Node *left; Node *right; Node *next; }
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
进阶:
你只能使用常量级额外空间。
使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
示例:
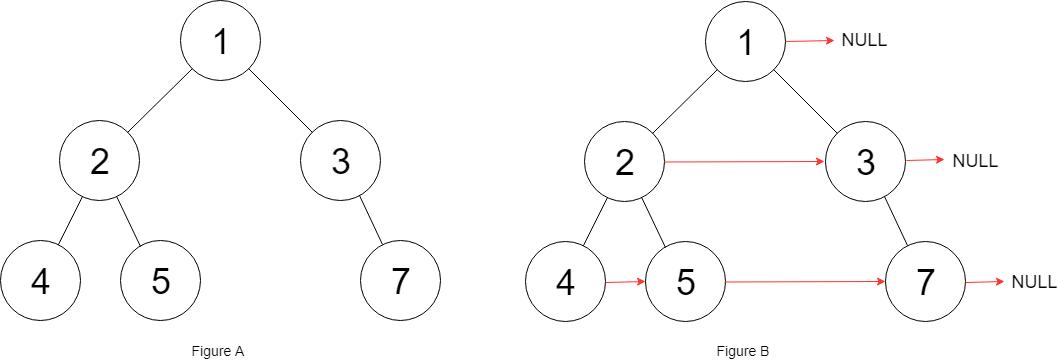
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。
提示:
树中的节点数小于 6000
-100 <= node.val <= 100
code:用bfs可以,但是要求常量空间复杂度,所以该解法略去,上一篇题解中写过。
与上一题不同的是,该树不为完全二叉树,比上一题的树更一般化,所以在连接一棵树的左右两棵子树时,需要先知道右子树的连接状态,因为root->next->left不一定存在,所以遍历顺序为根、右、左。
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {} }; */ class Solution { private: Node* getNextNode(Node* node) { while(node) { if(node->left) return node->left; if(node->right) return node->right; node=node->next; } return nullptr; } public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(root==nullptr) return root; if(root->left) { if(root->right) root->left->next=root->right; else root->left->next=getNextNode(root->next); } if(root->right) root->right->next=getNextNode(root->next); connect(root->right); connect(root->left); return root; } };