shiro是Apache公司的一个java 安全的框架,它功能强大、简单易用。
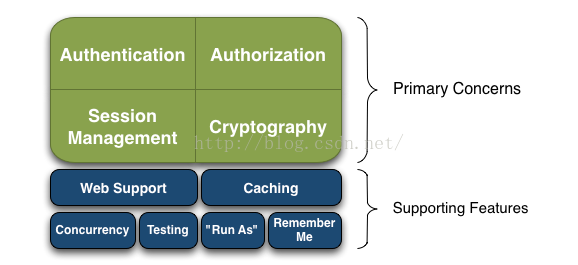
shiro的基本特征图如下:
主要模块有四个:
-
Authentication: Sometimes referred to as ‘login’, this is the act of proving a user is who they say they are.
-
Authorization: The process of access control, i.e. determining ‘who’ has access to ‘what’.
-
Session Management: Managing user-specific sessions, even in non-web or EJB applications.
-
Cryptography: Keeping data secure using cryptographic algorithms while still being easy to use.
Authentication: 身份认证
Authorization: 权限验证
Session Management: session管理
Cryptography: 加密
额外的支持功能- Web Support: Shiro’s web support APIs help easily secure web applications.
- Caching: Caching is a first-tier citizen in Apache Shiro’s API to ensure that security operations remain fast and efficient.
- Concurrency: Apache Shiro supports multi-threaded applications with its concurrency features.
- Testing: Test support exists to help you write unit and integration tests and ensure your code will be secured as expected.
- “Run As”: A feature that allows users to assume the identity of another user (if they are allowed), sometimes useful in administrative scenarios.
- “Remember Me”: Remember users’ identities across sessions so they only need to log in when mandatory.
Caching:缓存确保操作的安全和高效性
Concurrency:支持多线程
Testing:支持测试
Run As:允许用户承担另一个用户的身份(如果允许)的功能,有时在管理方案中很有用。
Remember Me:记住用户,下次直接登录。
上手操作
在eclipse中创建一个maven项目,命名为shiro01,在maven的配置文件pom.xml文件中引入shiro。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
会发现shiro-core核心jar包需要两个依赖包,而其中一个只是api,再引入slf4j
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-log4j12 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
下面开始模拟验证登录过程
1.在resource下创建一个属性文件shiro.ini,并编辑文件
[users]
liy313=123456
jack=123其它则是键值对:用户名=密码
2.编写java代码
package com.liy.shiro;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//读取配置文件,初始化SecurityManager工厂
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//获取SecurityManager实例
SecurityManager securityManager=factory.getInstance();
//把securityManager实例帮定到SecurityUtils中
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//得到当前执行的用户
Subject currentUser=SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建token用户令牌
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("liy313", "123456");
try {
//身份认证
currentUser.login(token);
System.out.println("用户验证成功");
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用户验证失败");
}
currentUser.logout();
}
}
http://shiro.apache.org/tutorial.html