填空题
战疫情
懂得如果确定枚举的边界非常重要
说是百元买百鸡的弱化版本
答案: 21

# 有困难的是确定x和y的范围
def check(x: int, y: int) -> bool:
if (2 * x + 100 * y == 50000) and (20000 <= (x + y) <= 21000):
return True
else:
return False
res = 0
for x in range(30000):
for y in range(1000):
if check(x, y): res += 1
print(res)
百元买百鸡
三变量可以只要两重循环,那么双变量也只要一重循环
# 5x + 3y +(1/3)z = 100
for x in range(1, 100 // 5 + 1):
for y in range(1, 100 // 3 + 1):
z = 100 - x - y
if 5 * x + 3 * y + (1 / 3) * z == 100:
print(x, y, z)
行动
很好方向模拟题目,很经典的问题
答案: -1010 1010
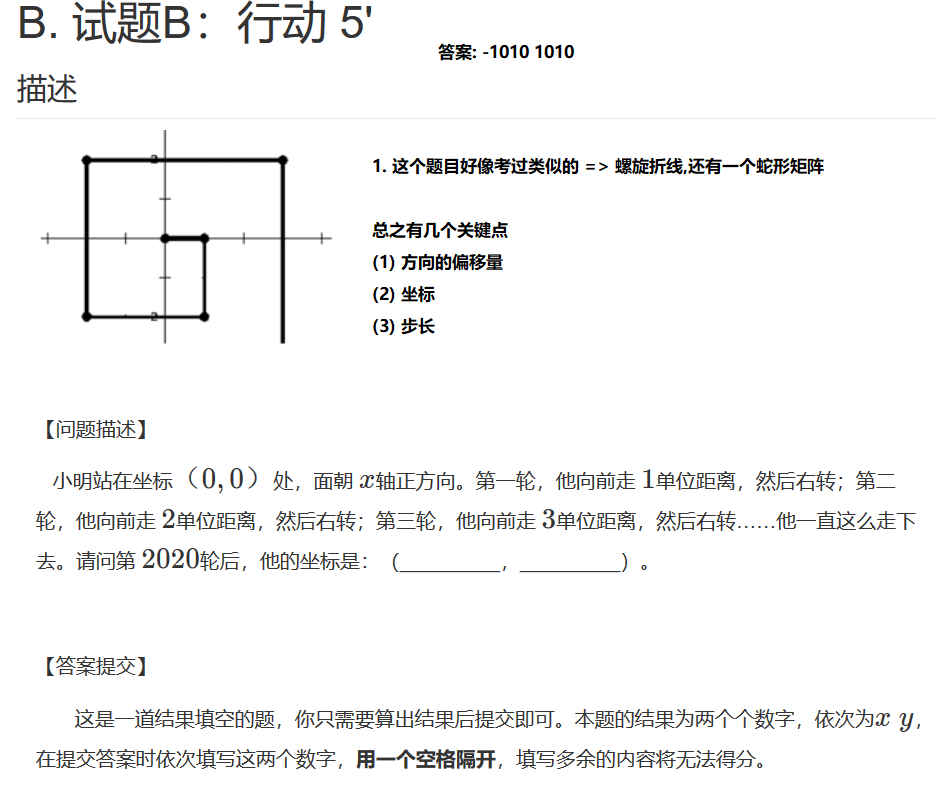
# 这是一个很经典的题目啊
dx = (+1, 0, -1, 0)
dy = (0, -1, 0, +1)
x, y = 0, 0 # 坐标
d = 0 # 方向
step = 1 # 步长
t = 2020 # 轮数
while t:
x += dx[d] * step
y += dy[d] * step
d = (d + 1) % 4
step += 1
t -= 1
print(x,y)
莱布尼茨公式
就是简单的循环迭代
但是C,Java要注意使用double,否则会因为精度问题出问题(至少15位往后)
答案: 3.141098
res = 0
t = 1
xishu = -1
while t <= 2020:
xishu *= -1
res += (xishu * 1 / (2 * t - 1))
t += 1
print("{:.6f}".format(4*res))
价值之和
两个经典题目组合 (1) 质数判断 (2) 约数

def is_p(x: int) -> bool:
if x in (0, 1): return False
i = 2
while i * i <= x:
if x % i == 0: return False
i += 1
return True
L = []
for i in range(100000):
if is_p(i): L.append(i)
# 返回x的质因数个数
def p_num(x: int) -> int:
s = set()
while not x == 1:
i = 0
while i < len(L) and x % L[i] != 0:
i += 1
s.add(L[i])
x //= L[i]
# print(s)
return len(s)
# 检查x是否包含5
def check(x: int) -> bool:
x = str(x)
if "5" in x:
return False
else:
return True
res = 0
for x in range(1, 2020 + 1):
if check(x):
res += p_num(x)
print(res)
判断质数
基础算法,请熟练

def is_p(x: int) -> bool:
i = 2
while i * i <= x:
if x % i == 0: return False
i += 1
return True
n = int(input().strip())
print("YES" if is_p(n) else "NO")
质因数
算术基本定理 + 求质数
L = [] # 素数表
res = [] # 答案
def is_p(x: int) -> bool:
i = 2
while i * i <= x:
if x % i == 0: return False
i += 1
return True
def p_num(x: int) -> set:
global L
s = set()
while not x == 1:
i = 0
while i < len(L) and x % L[i] != 0: i += 1
s.add(L[i])
x //= L[i]
return s
for i in range(2, 10000): # 数据范围只有1-1000
if is_p(i): L.append(i)
n = int(input().strip())
res.append(1)
res.append(n)
res.extend(p_num(n))
res.sort()
print(res)
数方
剪枝要趁早,Python不能算3次方
千万不要手算!! 直接计算机!!
答案: 729457169
package 竞码编程模拟赛;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class code05_数方 {
static List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<Integer>();
static boolean is_p(int x) {
for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++) {
if (x % i == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean is_c(int x) {
return Math.cbrt(x) == (int) Math.cbrt(x);
}
static boolean is_s(int x) {
return Math.sqrt(x) == (int) Math.sqrt(x);
}
static boolean is_f(int x) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.sqrt(x)) == (int) Math.sqrt(Math.sqrt(x));
}
static boolean is_t(int x) {
return T.contains(x);
}
static boolean is_h(int x) {
String s = x + "";
return s.equals(new StringBuilder(s).reverse().toString());
}
static void dfs(int u, String s) {
if (u == 9) {
if (is_s(Integer.valueOf(s.substring(6, 9)))
&& is_h(Integer.valueOf("" + s.charAt(2) + s.charAt(5)
+ s.charAt(8)))) {
System.out.println(s);
}
return;
}
if (u == 3) {
if (!is_c(Integer.valueOf(s.substring(0, 3)))) {
return;
}
}
if (u == 6) {
if (!is_p(Integer.valueOf(s.substring(3, 6)))) {
return;
}
}
if (u == 7) {
if (!is_t(Integer.valueOf("" + s.charAt(0) + s.charAt(3)
+ s.charAt(6)))) {
return;
}
}
if (u == 8) {
if (!is_f(Integer.valueOf("" + s.charAt(1) + s.charAt(4)
+ s.charAt(7)))) {
return;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
dfs(u + 1, s + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 三角数的处理
T.add(1);
for (int i = 0, t = 2; i < 100; i++) {
int x = T.get(i) + t;
T.add(x);
t += 1;
}
dfs(0, "");
}
}

