1. 背景知识
Prastudy Fauzi, Helger Lipmaa, and Bingsheng Zhang 2013年论文《Efficient Modular NIZK Arguments from Shift and Product》,提出:
- 基于shift-by-
argument 和 rotation-by-
argument构建permutation argument,相应的security reduce to the
assumption。
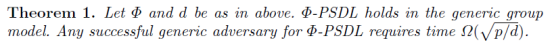
- Hadamard product argument
- SET-PARTITION argument,用于证明the prover knows a partition of the given set of integers to two sets that have the same sum。(可由2个product argument和1个shift argument组成。)
- SUBSET-SUM argument,用于证明the prover knows a non-zero subset of the given set of integers that sums to 0。性能要优于2010年论文《Short Pairing-Based Non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》和2012年论文《Progression-Free Sets and Sublinear Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》的CIRCUIT-SAT argument。
- DECISION-KNAPSACK argument,可基于SUBSET-SUM argument和range argument组合构建。
- scan argument(可由shift argument构建),用于证明one vector is the scan (or sum-of-all-prefixes) of another vector。
- range argument
- 采用FFT based polynomial multiplication to reduce the prover’s computation from to multiplications。
- 采用Pippenger’s[31] algorithm to speed up multi-exponentiations运算。

与2010年论文《Short Pairing-Based Non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》和2012年论文《Progression-Free Sets and Sublinear Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》的性能对比如下:



2. 多项式分解
Polynomial factorization in
can be done in polynomial time [25,230].
Let
be an efficient polynomial factorization algorithm that on input a degree-
polynomial
outputs all
roots of
。
3. Hadamard Product Argument
在2012年论文《Progression-Free Sets and Sublinear Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》的hadamard product argument的基础上,在CRS集合上做了优化,基本的算法思路仍然保持不变:


4. Shift and Rotation argument

可借助2010年论文《Short Pairing-Based Non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》中的permutation argument来证明,因为其中的permutation
为public known,只需要验证相应的
即可。





5. range argument

6. scan argument

scan argument(可由shift argument构建),用于证明one vector is the scan (or sum-of-all-prefixes) of another vector。
7. SET-PARTITION argument
SET-PARTITION argument,用于证明the prover knows a partition of the given set of integers to two sets that have the same sum。(可由2个product argument和1个shift argument组成。)


8. SUBSET-SUM argument
SUBSET-SUM argument,用于证明the prover knows a non-zero subset of the given set of integers that sums to 0。

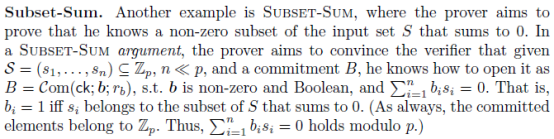

相比于2010年论文《Short Pairing-Based Non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》和2012年论文《Progression-Free Sets and Sublinear Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments》的CIRCUIT-SAT argument(需要
个product和permutation argument),SUBSET-SUM argument更简单且仅需要product argument和a more efficient right shift-by-1 argument (zero argument is trivial).
8.1 非零向量证明

9. DECISION-KNAPSACK argument
DECISION-KNAPSACK argument,可基于SUBSET-SUM argument和range argument组合构建。


参考资料:
[1] 2013年论文 Efficient Modular NIZK Arguments from Shift and Product
[2] ppt Efficient Modular NIZK Arguments from Shift and Product