The "eight queens puzzle" is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other. Thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal. The eight queens puzzle is an example of the more general N queens problem of placing N non-attacking queens on an N×N chessboard. (From Wikipedia - "Eight queens puzzle".)
Here you are NOT asked to solve the puzzles. Instead, you are supposed to judge whether or not a given configuration of the chessboard is a solution. To simplify the representation of a chessboard, let us assume that no two queens will be placed in the same column. Then a configuration can be represented by a simple integer sequence (Q1,Q2,⋯,QN), where Qi is the row number of the queen in the i-th column. For example, Figure 1 can be represented by (4, 6, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 5) and it is indeed a solution to the 8 queens puzzle; while Figure 2 can be represented by (4, 6, 7, 2, 8, 1, 9, 5, 3) and is NOT a 9 queens' solution.
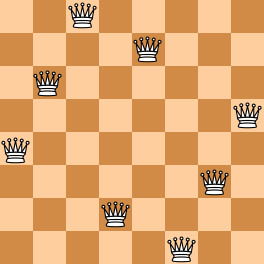 |
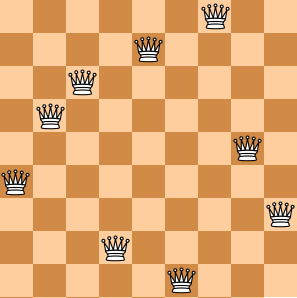 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives an integer K (1<K≤200). Then K lines follow, each gives a configuration in the format "N Q1 Q2 ... QN", where 4≤N≤1000 and it is guaranteed that 1≤Qi≤N for all i=1,⋯,N. The numbers are separated by spaces.
Output Specification:
For each configuration, if it is a solution to the N queens problem, print YES in a line; or NO if not.
Sample Input:
4
8 4 6 8 2 7 1 3 5
9 4 6 7 2 8 1 9 5 3
6 1 5 2 6 4 3
5 1 3 5 2 4
Sample Output:
YES
NO
NO
YES题目大意:给出一个n*n的棋盘,上面放上n个棋子,如果每一个棋子都不在同一列,同一行,同一斜线上,则输出“YES”否则输出“NO” 每一次有多组输入。
思路:1.由于输入的数列array中 任意array[i]=m表示该棋子放在第m行的第i列,根据数组下标递增的性质可知这n棋子在不同的列上,所以只需判断棋子是否在同一行,或者在同一斜线上。
2.为了降低复杂度,我们采用边输入边判断的方法,即判断已输入的棋子是否满足题意。我们用一个bool值flag=false来标记输入的数列是否满足题意,如果array[i]==array[j]则这两颗棋子在同一行,flag=true,如果array[i]和array[j]在同一斜线上,他们可以构成一个等腰直角三角形,所在行的差值等于所在列的差值。
难点:判断两个棋子是否在同一斜线上,解决方案利用等腰直角三角形,如果array[i]和array[j]在同一斜线上,他们可以构成一个等腰直角三角形,所在行的差值等于所在列的差值
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int k;
cin >> k;
while (k--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
bool flag = false;
vector<int>que(n + 1, 0);//记录输入的棋子坐标,角标为列坐标,内容为横坐标
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
cin >> que[i];
if (i > 1) {
for (int j = 1;j < i;j++) {
//判断是否在同一行
if (que[j] == que[i]) {
flag = true;
break;
}
//判断是否在同一斜线上
else {
if (abs(j - i) == abs(que[j] - que[i])) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
if (flag)
cout << "NO" << endl;
else
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
}