http://wiki.ros.org/smach/Tutorials/Getting%20Started
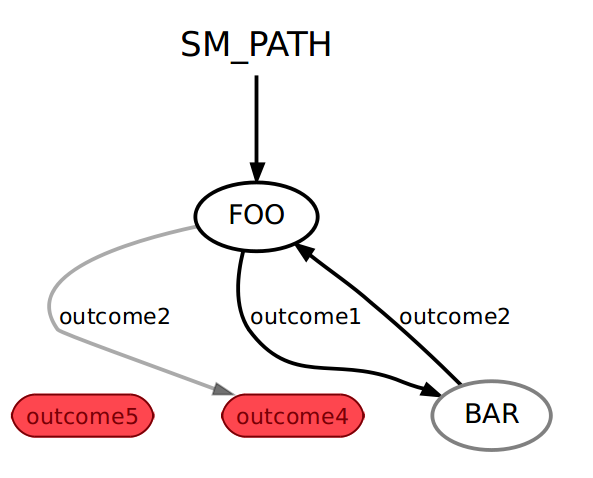
实现两个状态之间的转移,当经过outcome2时退出。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import smach
# define state Foo
class Foo(smach.State):
def __init__(self):
smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes=['outcome1','outcome2'])
self.counter = 0
def execute(self, userdata):
rospy.loginfo('Executing state FOO')
if self.counter < 3:
self.counter += 1
return 'outcome1'
else:
return 'outcome2'
# define state Bar
class Bar(smach.State):
def __init__(self):
smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes=['outcome2'])
def execute(self, userdata):
rospy.loginfo('Executing state BAR')
return 'outcome2'
# main
def main():
rospy.init_node('smach_example_state_machine')
# Create a SMACH state machine
sm = smach.StateMachine(outcomes=['outcome4', 'outcome5'])
# Open the container
with sm:
# Add states to the container
smach.StateMachine.add('FOO', Foo(),
transitions={'outcome1':'BAR',
'outcome2':'outcome4'})
smach.StateMachine.add('BAR', Bar(),
transitions={'outcome2':'FOO'})
# Execute SMACH plan
outcome = sm.execute()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()