# 最短路径算法 Dijkstra
# 输入:含权有向图 G=(V,E),V={1,2,3...n}
# 输出:G中顶点 1 到各个顶点地最短距离
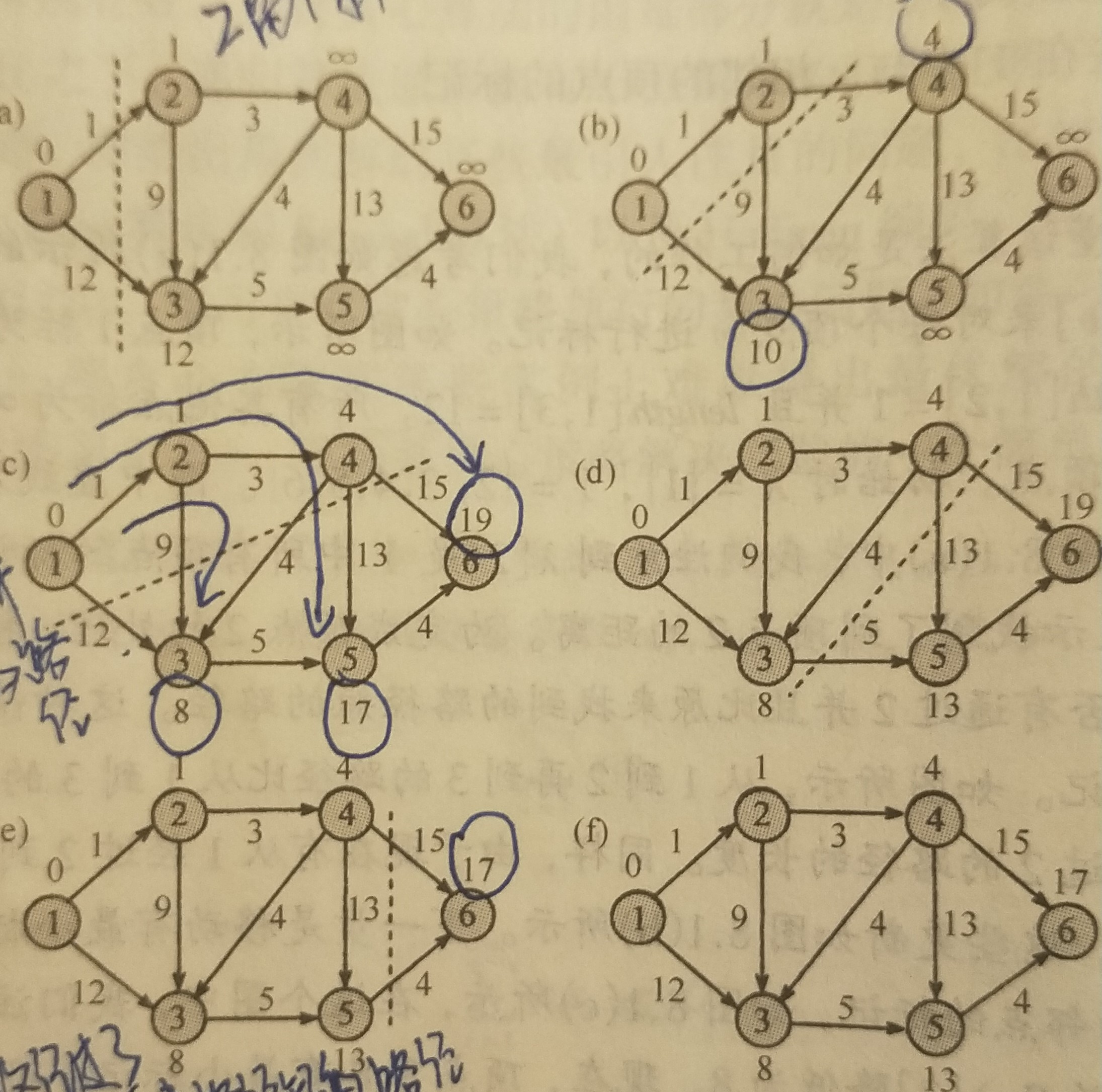
Dijkstra算法各点权值变化情况:
1 class Vertex: 2 #顶点类 3 def __init__(self,vid,outList): 4 self.vid = vid #出边 5 self.outList = outList #出边指向的顶点id的列表,也可以理解为邻接表 6 self.know = False #默认为假 7 self.dist = float('inf') #s到该点的距离,默认为无穷大 8 self.prev = 0 #上一个顶点的id,默认为0 9 def __eq__(self, other): 10 if isinstance(other, self.__class__): 11 return self.vid == other.vid 12 else: 13 return False 14 def __hash__(self): 15 return hash(self.vid)
1 #创建顶点对象 2 v1=Vertex(1,[2,3]) 3 v2=Vertex(2,[3,4]) 4 v3=Vertex(3,[5]) 5 v4=Vertex(4,[3,5,6]) 6 v5=Vertex(5,[6]) 7 v6=Vertex(6,[]) 8 9 #存储边的权值 10 edges = dict() 11 def add_edge(front,back,value): 12 edges[(front,back)]=value 13 add_edge(1,2,1) 14 add_edge(1,3,12) 15 add_edge(2,3,9) 16 add_edge(2,4,3) 17 add_edge(3,5,5) 18 add_edge(4,3,4) 19 add_edge(4,5,13) 20 add_edge(4,6,15) 21 add_edge(5,6,4)
1 #创建一个长度为7的数组,来存储顶点,0索引元素不存 2 vlist = [False,v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6] 3 #使用set代替优先队列,选择set主要是因为set有方便的remove方法 4 vset = set([v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6])
1 def get_unknown_min():#此函数则代替优先队列的出队操作 2 the_min = 0 3 the_index = 0 4 j = 0 5 for i in range(1,len(vlist)): 6 if(vlist[i].know is True): 7 continue 8 else: 9 if(j==0): 10 the_min = vlist[i].dist 11 the_index = i 12 else: 13 if(vlist[i].dist < the_min): 14 the_min = vlist[i].dist 15 the_index = i 16 j += 1 17 #此时已经找到了未知的最小的元素是谁 18 vset.remove(vlist[the_index])#相当于执行出队操作 19 return vlist[the_index]
1 def main(): 2 #将v1设为顶点 3 v1.dist = 0 4 5 while(len(vset)!=0): 6 v = get_unknown_min() 7 print(v.vid,v.dist,v.outList) 8 v.know = True 9 for w in v.outList:#w为索引 10 if(vlist[w].know is True): 11 continue 12 if(vlist[w].dist == float('inf')): 13 vlist[w].dist = v.dist + edges[(v.vid,w)] 14 vlist[w].prev = v.vid 15 else: 16 if((v.dist + edges[(v.vid,w)])<vlist[w].dist): 17 vlist[w].dist = v.dist + edges[(v.vid,w)] 18 vlist[w].prev = v.vid 19 else:#原路径长更小,没有必要更新 20 pass
函数调用:
1 main() 2 print('v.dist 即为从起始点到该点的最短路径长度:') 3 print('v1.prev:',v1.prev,'v1.dist',v1.dist) 4 print('v2.prev:',v2.prev,'v2.dist',v2.dist) 5 print('v3.prev:',v3.prev,'v3.dist',v3.dist) 6 print('v4.prev:',v4.prev,'v4.dist',v4.dist) 7 print('v5.prev:',v5.prev,'v5.dist',v5.dist) 8 print('v6.prev:',v6.prev,'v6.dist',v6.dist)
运行结果:
1 0 [2, 3] 2 1 [3, 4] 4 4 [3, 5, 6] 3 8 [5] 5 13 [6] 6 17 [] v.dist 即为从起始点到该点的最短路径长度: v1.prev: 0 v1.dist 0 v2.prev: 1 v2.dist 1 v3.prev: 4 v3.dist 8 v4.prev: 2 v4.dist 4 v5.prev: 3 v5.dist 13 v6.prev: 5 v6.dist 17
