二维数组中的查找
1.题目描述
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target。该矩阵具有以下特性:
每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例:
现有矩阵 matrix 如下:
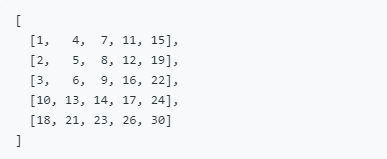
给定 target = 5,返回 true。
给定 target = 20,返回 false。
2.思路
因为二维数组每行每列都是递增的,从二维数组右上角开始比较,如果target < nums[row][col]则row++,
如果target > nums[row][col]则col–,否则就找到target。
3.代码
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
if(matrix.empty()){
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.size();
int cols = matrix[0].size();
int row = 0;
int col = cols - 1;
while(row < rows && col >= 0){
if(matrix[row][col] == target){
return true;
}
else if(matrix[row][col] > target){
col--;
}
else{
row++;
}
}
return false;
}
};
4.复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n+m)。
时间复杂度分析的关键是注意到在每次迭代(我们不返回 true)时,行或列都会精确地递减/递增一次。由于行只能增加 m 次,而列只能减少n 次,因此在导致 while 循环终止之前,循环不能运行超过 n+m 次。因为所有其他的工作都是常数,所以总的时间复杂度在矩阵维数之和中是线性的。
空间复杂度:O(1),因为这种方法只处理几个指针,所以它的内存占用是恒定的。
